题目0x1 主要记录解题中一些stl的函数
[toc]
字符串处理 使用string标准库
当使用getline(cin,string)时,如果前面有cin>>,注意吸收换行符。
substr(a,b);
返回a开始的b个字符
erase(a); earse(a,b)
移除a之后的字符; 移除a开始的b个字符
find(“a”,b);
从前向后查找a第一次出现的位置, b(可选)查找开始的下标 ,找不到时返回值-1
rfind(“a”)
从后向前查找a第一次出现的位置。
find.first_of(“abcd”)
从前向后查找abcd任一字符第一次出现的位置
find.last_of(“abcd”)
从前向后查找abcd任一字符最后一次出现的位置
find_first_not_of(“abcd”)
不在”abcd”中的字母第一次出现的地方。
find_last_not_of(“abcd”)
不在”abcd”中的字母最后一次出现的地方。
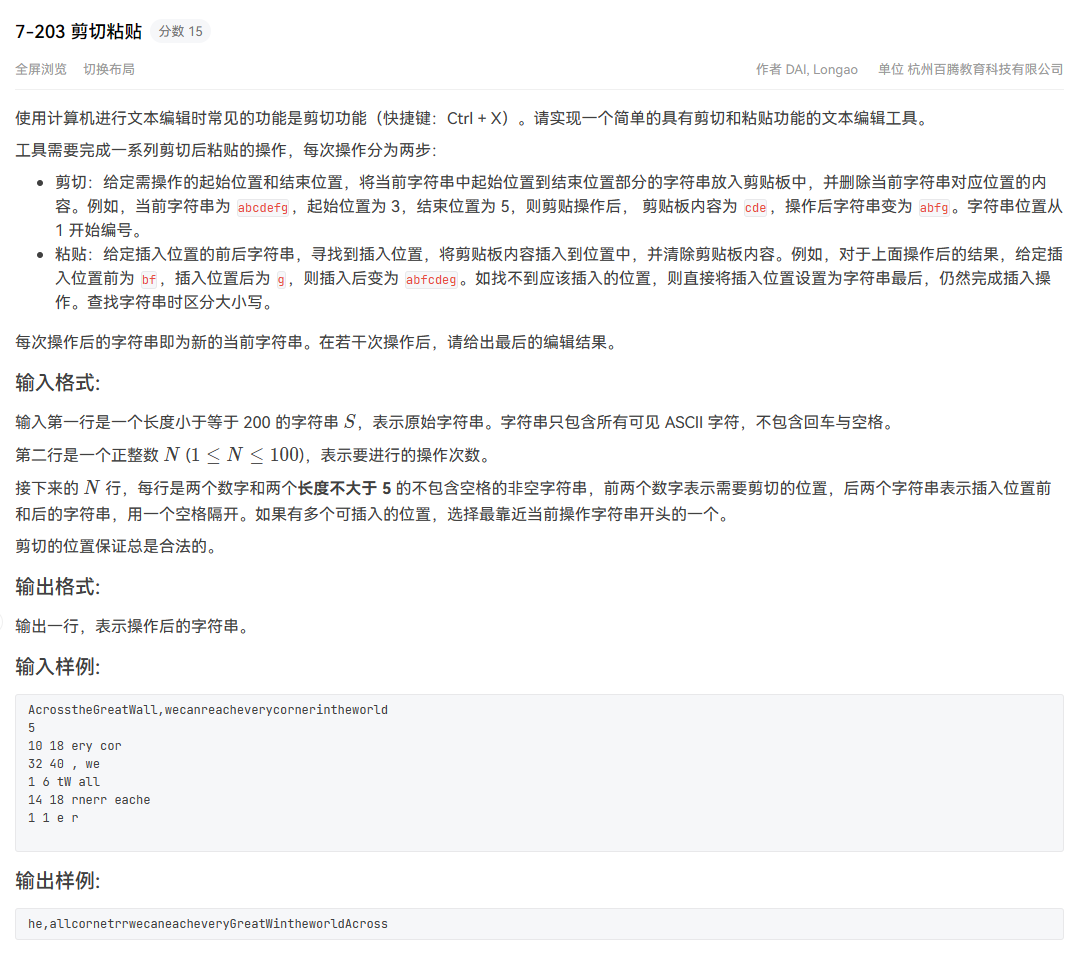
剪切粘贴 照着题目写代码,注意下字符串匹配返回的是字串的首地址就OK了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;int main () std::string S; int n; cin >> S >> n; while (n--) { std::string s1, s2, tmp, tmp1, ss; int a, b; int pos; cin >> a >> b >> s1 >> s2; a--, b--; tmp = S.substr (a, b - a + 1 ); S.erase (a, b - a + 1 ); ss = s1 + s2; if ((pos = S.find (ss)) == string::npos) { S += tmp; } else { tmp1 = S.substr (0 , pos); tmp1 += s1; tmp1 += tmp; tmp1 += S.substr (pos+s1.l ength(), S.length () - pos - s1.l ength()); S = tmp1; } } cout << S << endl; return 0 ; }
估值一亿的AI核心代码 使用正则表达式 塔 栈,启动!
empty()
判断是否为空,空返回true,否则返回false
size()
返回元素个数,类型为size_t
push(x)
将x压栈
top()
返回栈顶元素
pop()
从栈顶删除元素,注意没有返回值,
emplace(x)
将x压栈
push和emplace的区别:emplace只调用一次构造函数,而push会调用一次构造函数+一次移动构造函数。即emplace使用了移动构造函数,直接在容器内构造对象。而push需要先构造对象,再push到容器中。由于省去了拷贝构造过程,emplace一般比push快。
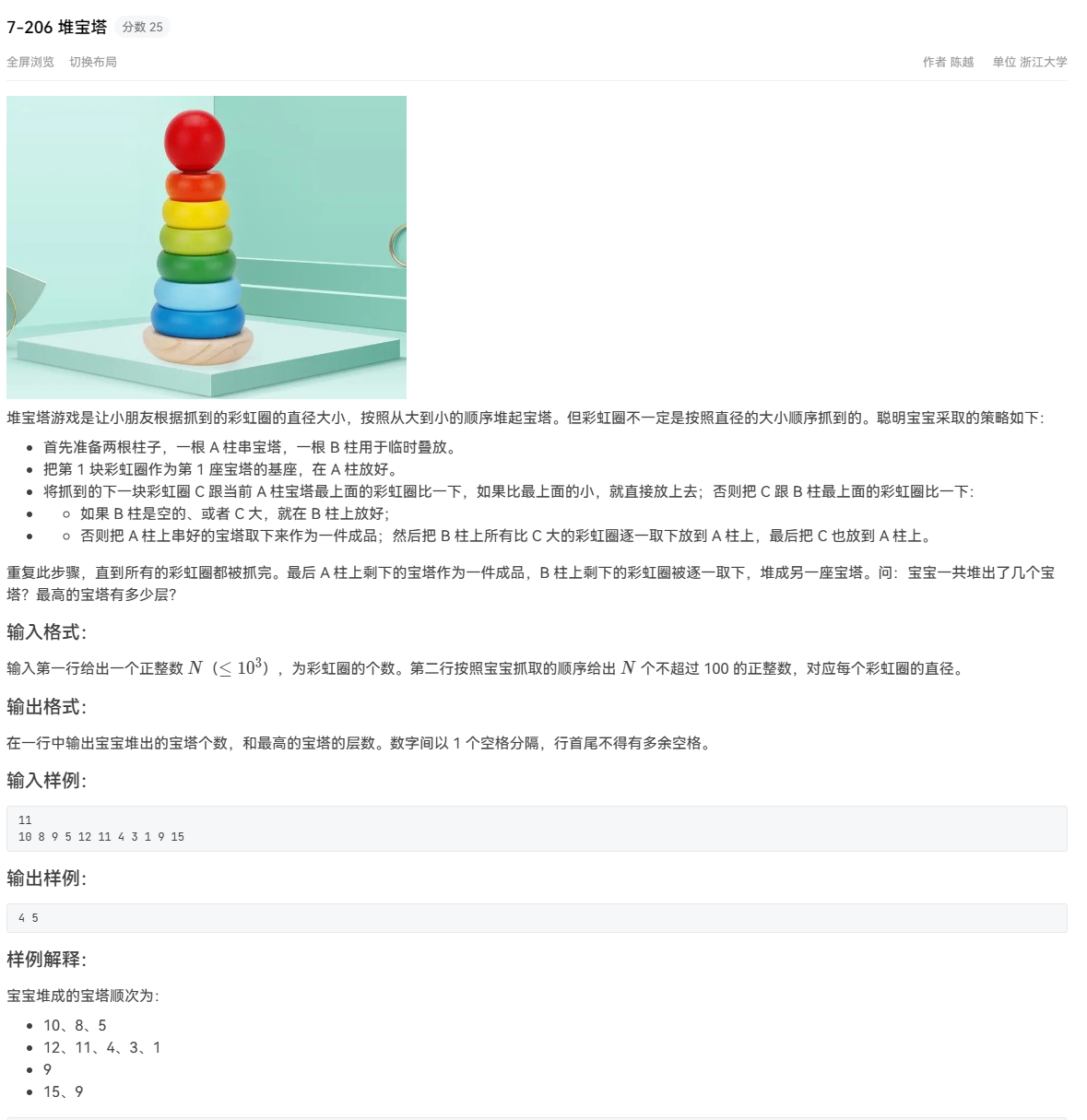
堆宝塔 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std;int main () int N, in, Tower = 0 , hight = 0 ; stack <int > a, b; cin >> N; while (N--) { cin >> in; if (a.empty ()) a.push (in); else if (in < a.top ()) a.push (in); else if (b.empty () || b.top () < in) b.push (in); else { Tower++; hight = max (hight, (int )a.size ()); while (!a.empty ()) { a.pop (); } while (!b.empty () && b.top () > in) { a.push ((int )b.top ()); b.pop (); } a.push (in); } } if (!a.empty ()) { hight = max (hight, (int )a.size ()); Tower++; } if (!b.empty ()) { hight = max (hight, (int )b.size ()); Tower++; } cout << Tower << " " << hight << endl; return 0 ; }
汉诺塔 //TODO
set 此标头是容器 库的一部分,是一个内部自动有序 且不含重复元素 的容器,因此我们要通过迭代器来访问set内的元素。
insert()
插入容器
find(value)
查找元素,如果找到了该元素,则返回指向该元素的迭代器;如果没有找到,则返回一个指向集合末尾的迭代器(即 end())。
earse(value)
删除值为value的元素
erase(first, last)
删除一个区间内的所有元素。
size()
set内元素个数
clear()
清空set
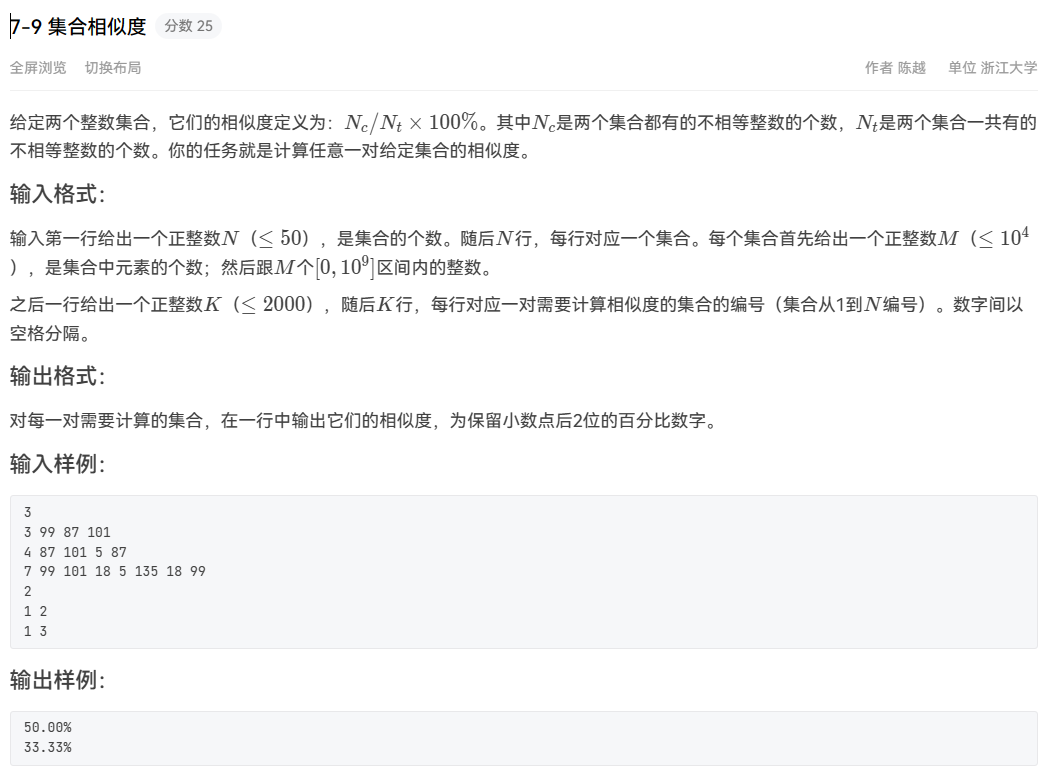
集合相似度 参考:L2-005 集合相似度_题目描述 给定两个整数集合,它们的相似度定义为:nc/nt×100%。其中nc是两个集合都-CSDN博客
要注意一下这题相似度的计算公式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <iostream> #include <set> using namespace std;const int N = 55 ;int main () int n; set<int > jihe[55 ]; cin >> n; int pos = 1 ; while (n--) { int tmp; cin >> tmp; while (tmp--) { int tmp2; cin >> tmp2; jihe[pos].insert (tmp2); } pos++; } int m ; cin >> m; while (m--) { int a, b, count = 0 ; cin >> a >> b; int tmp = jihe[a].size () + jihe[b].size (); for (auto it : jihe[a]) { if (jihe[b].find (it) != jihe[b].end ()) { count++; } } double p = count * 100.0 / (tmp - count); printf ("%.2f%\n" , p); count = 0 ; } return 0 ; }
队列 普通队列
top()
访问队首元素
empty()
队列是否为空
size()
返回队列内元素个数
push(a)
队尾插入元素a
emplace()
构造一个元素并插入队列
pop()
弹出队头元素
swap(other)
与other交换内容
优先队列 不同于普通队列,优先队列元素的出队顺序不是按照它们进入队列的顺序,而是根据它们的优先级来确定的。
priority_queue q;
默认情况下是最大值优先队列
priority_queue ,greater > q;
最大值优先队列
priority_queue ,less >q;
最小值优先队列
天梯赛的赛场安排 这题在比赛的时候没做出来,好吧复盘我么没做出来,分析下来是需要我们认真读题。我们看n<C的情况,需要取n最小,即没有座位的考生人数最小的组优先安排赛场,然后再插入其他组,若其他组加入后容量大于所有组的赛场容量,则新开一个赛场。(PS:这就是为什么不能直接直接将考生整除C,因为这样分配有些考场会有空座位)。
那么根据题意我们用优先队列解决问题。
参考:L2-2 天梯赛的赛场安排(C++注释版)-CSDN博客
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <queue> const int MAX_N = 5005 ;int a[MAX_N];using namespace std;int main () int N, C; int count = 0 , cnt = 0 ; priority_queue<int > q; cin >> N >> C; while (N--) { std::string name; int num,kaochang; cin >> name >> num; kaochang = ceil (1.0 *num / C); count += num / C; cout << name << " " << kaochang << endl; if (num % C ) { q.emplace (num%C); } } while (!q.empty ()) { int tmp = q.top (); q.pop (); bool flag = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < cnt; i++) { if (a[i] + tmp <= C) { a[i] += tmp, flag = false ; break ; } } if (flag) a[cnt++] = tmp; } cout << cnt+count << endl; return 0 ; }
others 取整函数 注意这些函数的返回值都为double,通过隐式转换为int和float。
floor(x)
把一个小数向下取整
ceil(x)
把一个小数向上取整
round(x)
把一个小数四舍五入
数字字母判断,大小转换 #include<cctype>
isdigit()
是否为数字
isalpha()
是否未字母
isalnum()
是否为数字或者字母
.islower()
是否为小写字母
isupper()
是否为大写字母
toupper(a)
转换为大写字母
tolower(a)
转换为小写字母
分寝室 比赛没有做出来这题,赛后总结一下,思路是对的,但是具体实现还有问题,总结就是——还要多练!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;int main () int n0, n1, n; cin >> n0 >> n1 >> n; int flag = 0 ; int min = 100005 ; int min_i; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n && i < n0 && (n - i) < n1; i++) { if (n0 % i == 0 && n1 % (n - i) == 0 ) { flag = 1 ; int tmp = abs (n0 / i - n1 / (n - i)); if (tmp < min) { min = tmp; min_i = i; } } } if (flag) { cout << min_i << " " << n - min_i << endl; } else { cout << "No Solution" << endl; } return 0 ; }
单身狗 PTA 1065 单身狗 (25 分) C++实现_找出单身狗c++-CSDN博客
Manacher(马拉车)(求解回文串) 参考:Manacher - OI Wiki (oi-wiki.org)
L2-008 最长对称子串(25 分)-CSDN博客
最长对称字串 有点难理解,自己需要自己手动模拟下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;string s; int p[2010 ];int main () string s; getline (cin, s); int len = s.length (), id = 0 , maxlen = 0 ; for (int i = len; i >= 0 ; --i) { s[2 * i + 2 ] = s[i]; s[2 * i + 1 ] = '#' ; } s[0 ] = '*' ; for (int i = 2 ; i < 2 * len + 1 ; ++i) { if (p[id] + id > i) p[i] = p[2 * id - i] < p[id] + id - i ? p[2 * id - i] : p[id] + id - i; else p[i] = 1 ; while (s[i - p[i]] == s[i + p[i]]) ++p[i]; if (id + p[id] < i + p[i]) id = i; if (maxlen < p[i]) maxlen = p[i]; } cout << maxlen - 1 << endl; return 0 ; }
7-209 寻宝图 通过这题可以很好学习dfs和bfs解法
BFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <utility> using namespace std;typedef pair<int ,int > pa;const int N = 100005 ;string arr[N]; int land = 0 ; int treasure = 0 ; int xway[4 ] = {-1 ,0 ,0 ,1 }; int yway[4 ] = {0 ,1 ,-1 ,0 };int n,m;void bfs (int x,int y) land++; bool flag = false ; if (arr[x][y]!='1' ) flag = true ; queue<pa> qu; qu.push ({x,y}); while (!qu.empty ()) { auto pos = qu.front (); qu.pop (); if (arr[pos.first][pos.second] == '0' ) continue ; if (arr[pos.first][pos.second] != '1' ) flag = true ; arr[pos.first][pos.second] = '0' ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int xx = pos.first + xway[i]; int yy = pos.second + yway[i]; if (xx>=0 && xx<n && yy>=0 && yy < m) qu.push ({xx,yy}); } } if (flag) treasure++; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) cin >> arr[i]; for (int i = 0 ; i <n; i++) for (int j = 0 ; j <m; j++) { if (arr[i][j] != '0' ) bfs (i,j); } cout << land << " " << treasure << endl; }
DFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int MAXN=100005 ;string arr[MAXN]; int n,m;int xway[]={1 ,0 ,-1 ,0 };int yway[]={0 ,1 ,0 ,-1 };int land = 0 ;int treasure = 0 ;bool flag = false ;void dfs (int x, int y) if (arr[x][y] == '0' ) return ; if (arr[x][y] != '1' ) flag = true ; arr[x][y] = '0' ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int xx = x + xway[i]; int yy = y + yway[i]; if (xx>=0 && xx<n && yy>=0 && yy<m) dfs (x+xway[i],y+yway[i]); } return ; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i<n;i++) cin >> arr[i]; for (int i = 0 ; i<n;i++) for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) { if (arr[i][j] != '0' ) { flag = false ; dfs (i,j); if (flag) treasure++; land++; } } cout << land << " " << treasure << endl; }