贪心 TODO:畜栏预定、雷达设备
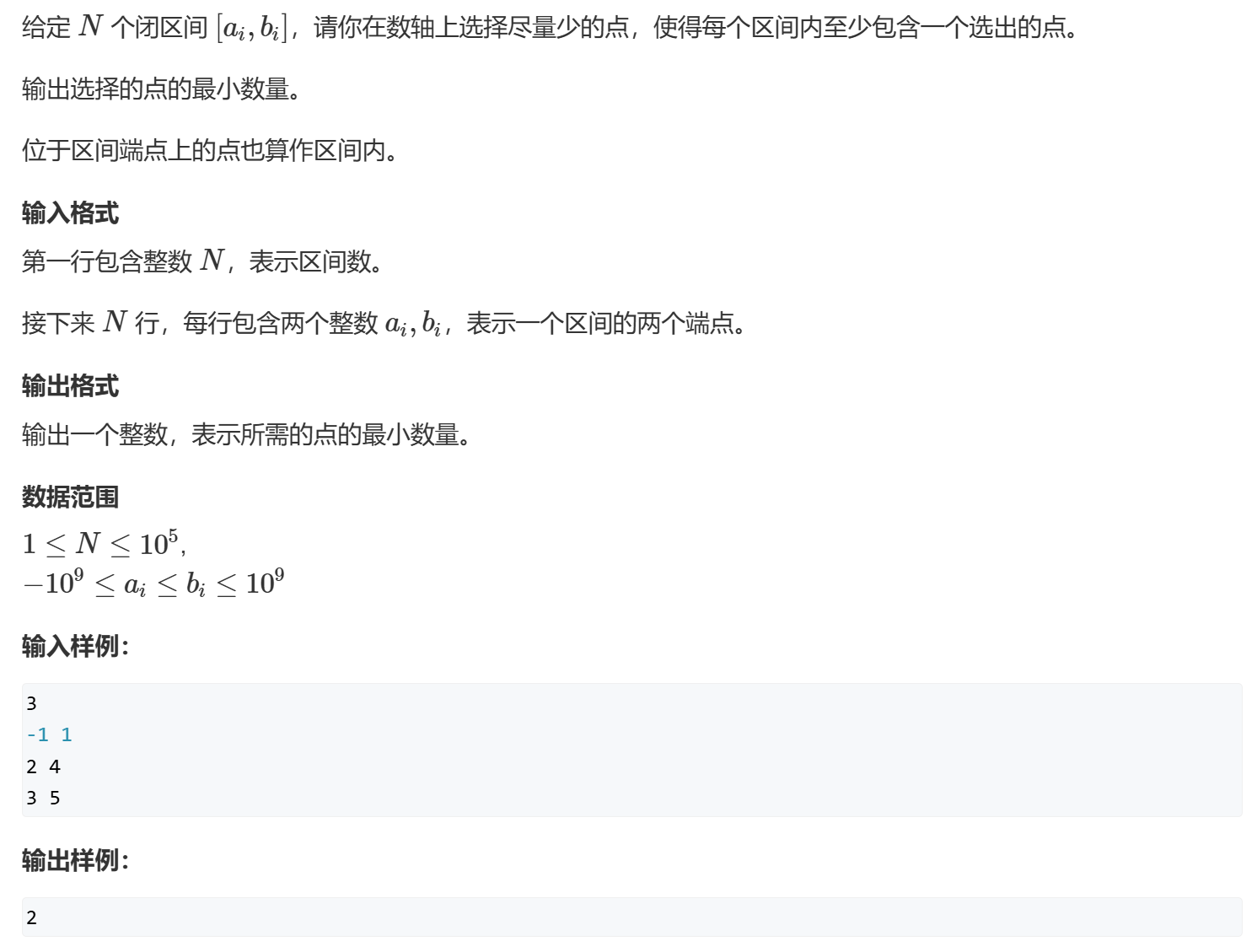
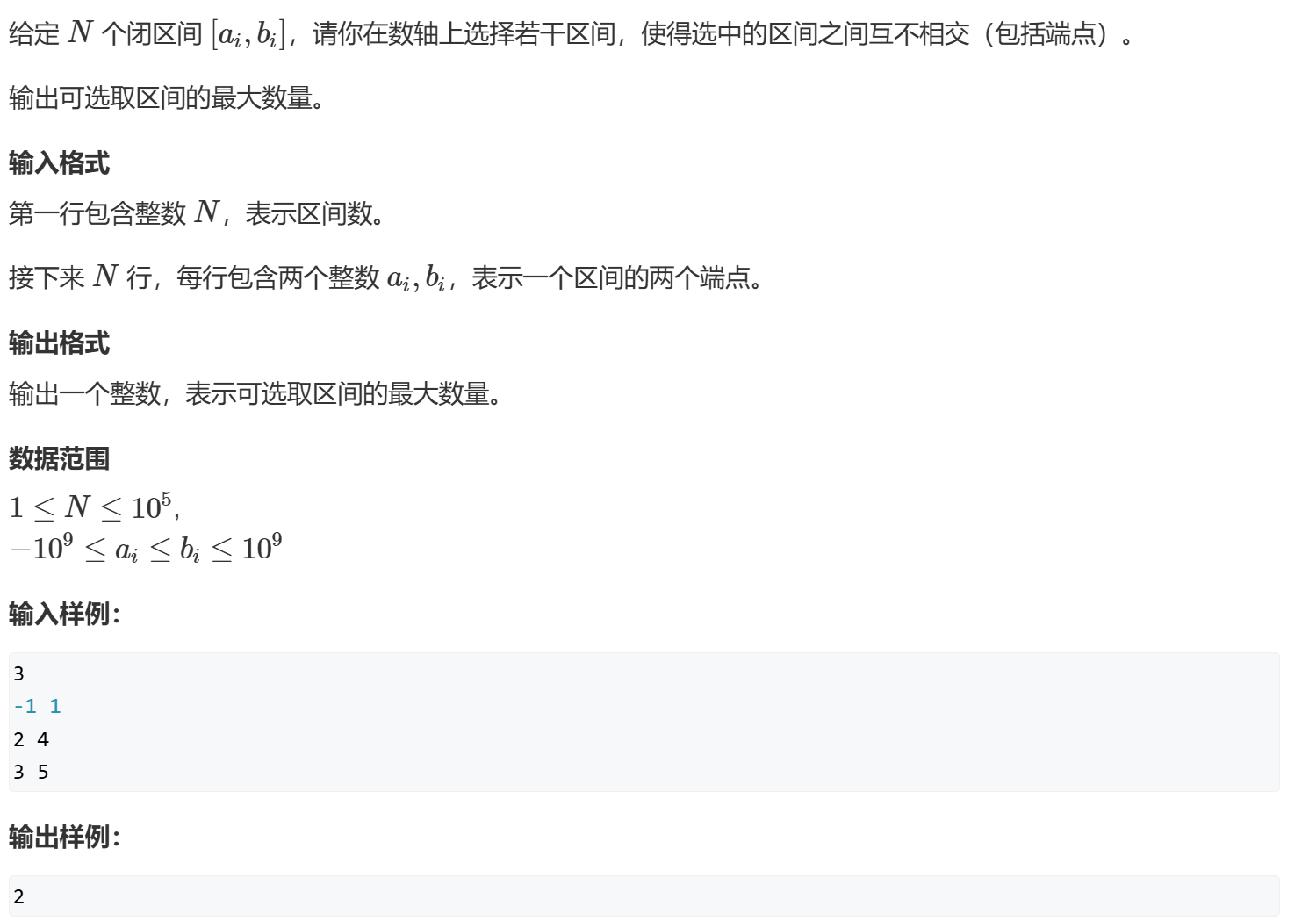
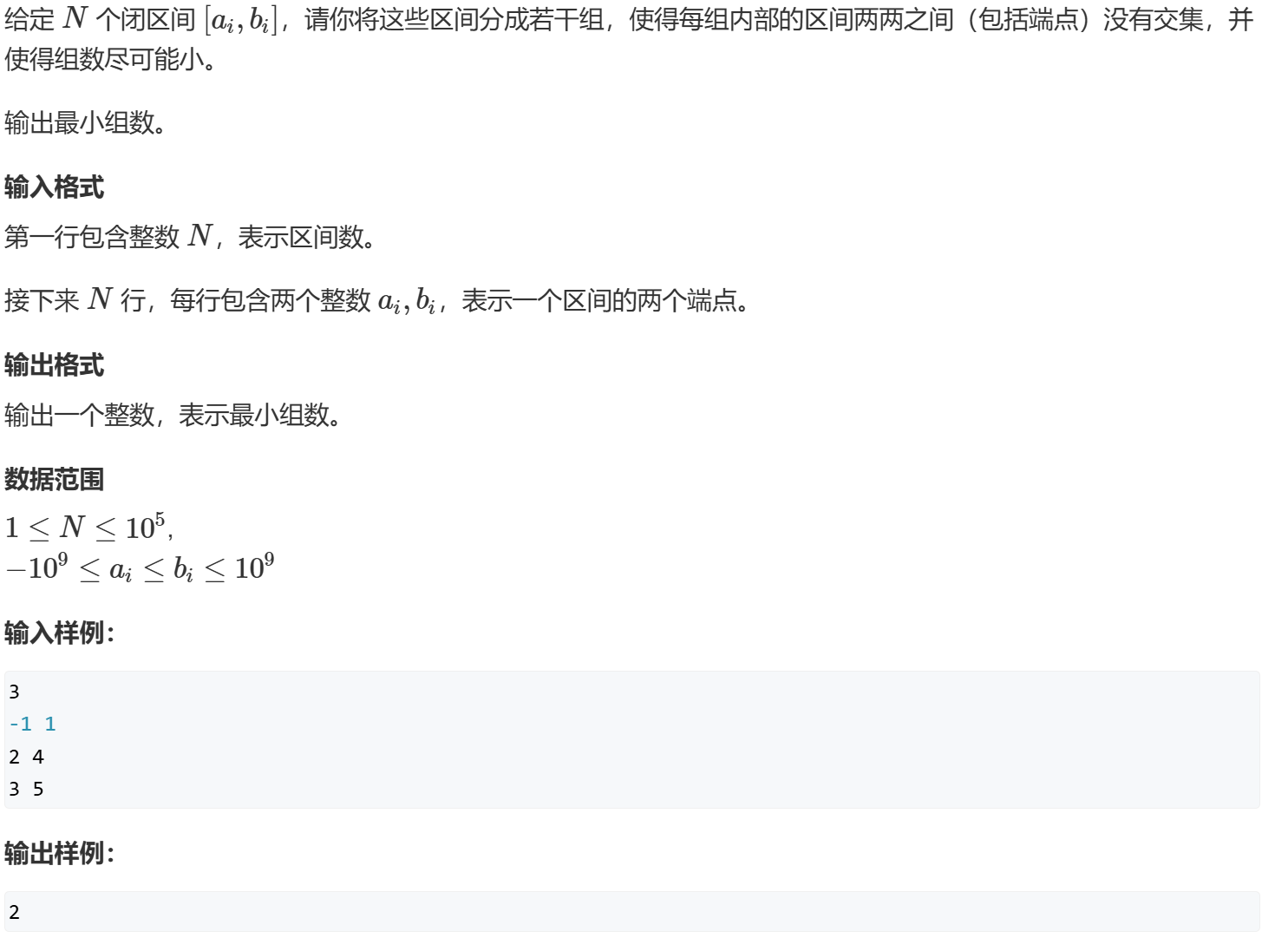
区间问题 贪心题的要点:
acwing905 我们通过重载运算符,设置为通过右端点从小到大排序,获取第一个右端点最大值为max值,若其他线段的左端点小于该max值,则continue。若大于则更新max值,res++。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 ;struct st { int lef; int rig; bool operator <(const st &tmp) const { return this ->rig < tmp.rig; } } st[N]; int main () int n; cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cin >> st[i].lef >> st[i].rig; } sort (st, st + n); int max = -2e9 ; int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (st[i].lef > max) { max = st[i].rig; res++; } } cout << res << endl; }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 from functools import cmp_to_keyclass point : def __init__ (self,a,b ): self .a = a self .b = b def cmp (x, y ): if x.b != y.b: return x.b - y.b return x.a - y.a n = int (input ()) points = [] for i in range (n): a,b = map (int ,input ().split()) points.append(point(a,b)) points.sort(key=cmp_to_key(cmp)) cnt = 0 right = -1e9 -10 for i in range (n): if points[i].a > right: cnt += 1 right = points[i].b print (cnt)
acwing908 这题可以采用右端点排序,也可以采用左端点排序。
cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 5 ;struct st { int lef; int rig; bool operator < (const st& tmp) const { return this ->rig < tmp.rig; } }st[N]; int main () int n; cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cin >> st[i].lef >> st[i].rig; } sort (st,st + n); int res = 0 ; int rigmax = -2e9 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) { if (st[i].lef > rigmax) { rigmax = st[i].rig; res ++; } } cout << res << endl; }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from functools import cmp_to_keyclass point : def __init__ (self,a,b ): self .a = a self .b = b def cmp (x, y ): if x.b != y.b: return x.b - y.b return y.a - x.a points = [] n = int (input ()) for i in range (n): a,b = map (int ,input ().split()) points.append(point(a,b)) points.sort(key=cmp_to_key(cmp)) righ = -1e9 -10 cnt = 0 for i in range (n): if points[i].a > righ: cnt += 1 righ = points[i].b print (cnt)
区间选点问题和最大不相交区间数量的区别
按右端点排序 保证贪心最优性跨过当前右端点 的区间都会被后续的点覆盖计数逻辑 在数学上完全等价
acwing906 python 贪心
按左端点排序,保证正向遍历时区间是稠密的
我们通过优先队列模拟小根堆,小根堆堆顶维护当前组右端点的最小值(若最小值都无法插入,则其他组也无法插入该区间)
能插入,更新堆顶为当前区间右端点
不能插入,插入当前区间右端点
此时堆重新排序,产生新的右端点最小值
为什么不能为大根堆:
小根堆 :保证每次选择最小的右端点,覆盖尽可能多的区间,得到最少点数。等价于选择最早结束的区间。大根堆 :会错过更优的覆盖机会,导致点数增加。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 from queue import PriorityQueue from functools import cmp_to_key n = int (input ()) class Node: def __init__(self,a,b): self.a = a self.b = b class lefnode: def __init__(self,p): self.p = p def __lt__(self,other): return self.p < other.p def cmp (x,y): return x.a - y.a nodes = [] for i in range (n): a,b = map (int ,input ().split ()) nodes.append (Node (a,b)) nodes.sort (key=cmp_to_key (cmp)) # for i in range(n): # print(nodes[i].a,nodes[i].b) q = PriorityQueue () q.put (lefnode (-1e9 -10 )) for i in range (n): x = q.get () if q.empty () or x.p >= nodes[i].a: q.put (x) q.put (lefnode (nodes[i].b)) else : q.put (lefnode (nodes[i].b)) # for i in range(n): # q.put(nodes[i]) print (q.qsize ())
差分 参考题解AcWing 906. 区间分组(200 +ms) - AcWing
这题也属于区间重叠问题,使用不用数组的差分思想(扫描线算法)
将区间覆盖转化为”开始”和”结束”事件
通过+1和-1表示覆盖变化
(a, 1):表示在坐标 a 处有一个区间开始
(b+1, -1):表示在坐标 b+1 处有一个区间结束ans += b:根据事件类型调整当前重叠数maxans = max(maxans, ans):记录最大值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 n = int (input ()) arr = [] for i in range (n): a,b = map (int ,input ().split()) arr.append((a,1 )) arr.append((b+1 ,-1 )) arr.sort(reverse = False ) ans = 0 maxans = 0 for a,b in arr: ans += b maxans = max (maxans,ans) print (maxans)
Huffman树 acwing148 哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding)是一种贪心算法 的应用,用于构造最优前缀码,实现数据的高效压缩。其核心思想是:频率越高的字符,分配的编码越短 。
哈夫曼算法通过以下步骤实现贪心选择:
将字符按频率升序排序 。每次合并频率最小的两个节点 ,生成新节点(频率为两者之和)。重复合并 ,直到只剩一个根节点。
贪心选择性质 :每次合并当前最小的两个节点,保证局部最优导致全局最优。
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 from queue import PriorityQueuen = int (input ()) heap = PriorityQueue() arr = list (map (int ,input ().split())) for i in arr: heap.put(i) res = 0 while heap.qsize() > 1 : a = heap.get() b = heap.get() res += a+b heap.put(a+b) print (res)
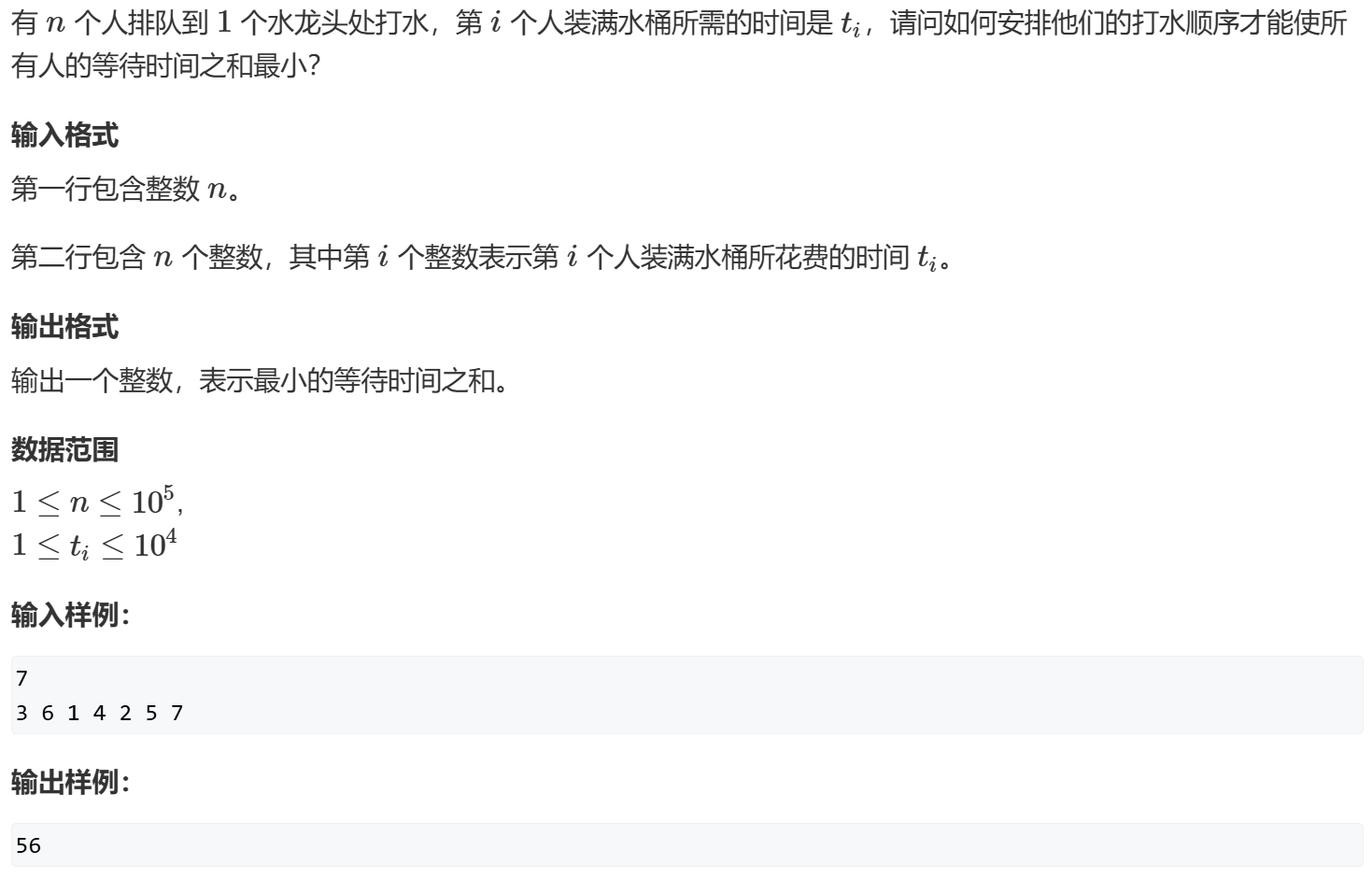
排序不等式 acwing913 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 n = int (input ()) t = list (map (int , input ().split())) t.sort() total_time = 0 for i in range (n): total_time += t[i] * (n - i - 1 ) print (total_time)
AcWing 104. 货仓选址 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 n = int (input ()) arr = list (map (int , input ().split())) arr.sort() median = arr[n // 2 ] total_distance = sum (abs (x - median) for x in arr) print (total_distance)
对于两个