[toc]
acwing826. 单链表 头插法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N = 100005 ;int head, e[N], ne[N], idx; void init () head = -1 ; idx = 0 ; } void add_to_head (int x ) e[idx] = x; ne[idx] = head; head = idx; idx ++; } void remove (int pos) ne[pos] = ne[ne[pos]]; } void insert (int x, int pos) e[idx] = x; ne[idx] = ne[pos]; ne[pos] = idx; idx++; } int main () int m; cin >> m; init (); while (m--) { char op; int pos, x; cin >> op; if (op == 'H' ) { cin >> x; add_to_head (x); } else if (op == 'D' ) { cin >> pos; if (!pos) head = ne[head]; else remove (pos - 1 ); } else { cin >> pos >> x; insert (x, pos -1 ); } } for (int i = head; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) cout << e[i] << " " ; cout<< endl; }
827.双链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 5 ;int l[N], r[N], e[N];int idx;void init () l[1 ] = 0 ; r[0 ] = 1 ; idx = 2 ; } void add (int k, int x) e[idx] = x; r[idx] = r[k]; l[idx] = k; l[r[idx]] = idx; r[k] = idx; idx++; } void remove (int k) r[l[k]] = r[k]; l[r[k]] = l[k]; } int main () int m; cin >> m; init (); while (m--) { string op; cin >> op; int k, x; if (op == "R" ) { cin >> x; add (l[1 ], x); } else if (op == "L" ) { cin >> x; add (0 , x); } else if (op == "D" ) { cin >> k; remove (k + 1 ); } else if (op == "IL" ) { cin >> k >> x; add (l[k + 1 ], x); } else if (op == "IR" ) { cin >> k >> x; add (k + 1 , x); } } for (int i = r[0 ]; i != 1 ; i = r[i]) cout << e[i] << ' ' ; return 0 ; }
828.模拟栈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 ;int st[N];int top = -1 ;int n;int main () cin >> n; while (n -- ) { string s; cin >> s; if (s == "push" ) { cin >> st[++top]; } if (s == "query" ) { cout << st[top] << endl; } if (s == "pop" ) { top--; } if (s == "empty" ) { if (top == -1 ) cout << "YES" << endl; else cout << "NO" << endl; } } return 0 ; }
3302. 表达式求值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 #include <iostream> #include <stack> #include <string> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std;stack<int > num; stack<char > op; unordered_map<char , int > h{{'+' , 1 }, {'-' , 1 }, {'*' , 2 }, {'/' , 2 }}; void eval () int a = num.top (); num.pop (); int b = num.top (); num.pop (); char c = op.top (); op.pop (); int res = 0 ; if (c == '+' ) res = b + a; if (c == '-' ) res = b - a; if (c == '*' ) res = b * a; if (c == '/' ) res = b / a; num.push (res); } int main () string s; cin >> s; int idx = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.size (); i++) { if (isdigit (s[i])) { int j = i, res = 0 ; while (j < s.size () && isdigit (s[j])) { res = res * 10 + (s[j] - '0' ); j++; } i = j - 1 ; num.push (res); } else if (s[i] == '(' ) { op.push ('(' ); } else if (s[i] == ')' ) { while (op.top () != '(' ) { eval (); } op.pop (); } else if (h.count (s[i])) { while (op.size () && h[op.top ()] >= h[s[i]]) eval (); op.push (s[i]); } } while (op.size ()) eval (); cout << num.top () << endl; return 0 ; }
829. 模拟队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100005 ;int q[N];int hh = 0 ;int tt = -1 ;int main () int n; string s; cin >> n; while (n--) { cin >> s; if (s == "push" ) { cin >> q[++tt]; } if (s == "pop" ) { hh++; } if (s == "query" ) { cout << q[hh] << endl; } if (s == "empty" ) { if (hh > tt) cout << "YES" << endl; else cout << "NO" << endl; } } }
830. 单调栈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std;stack<int > st; int main () int n, tmp; cin >> n; st.push (-1 ); while (n--) { cin >> tmp; while (tmp <= st.top ()) st.pop (); cout << st.top () << " " ; st.push (tmp); } }
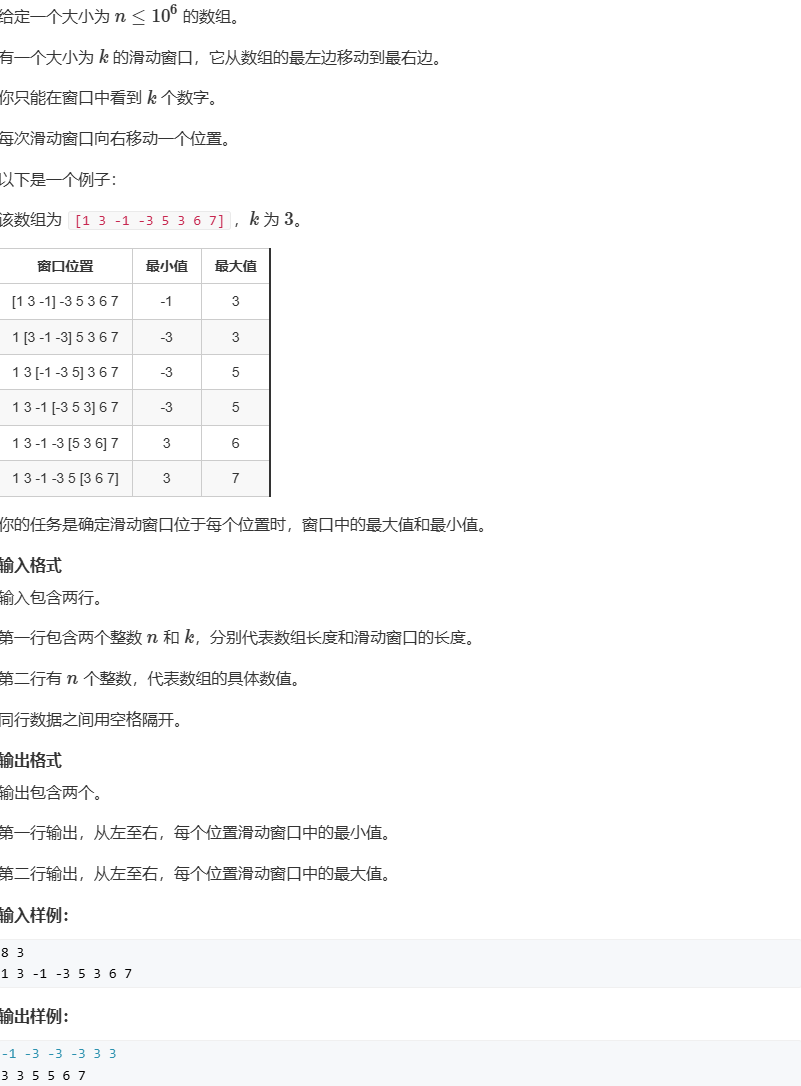
154 滑动窗口 通过在队头维持当前窗口的最小值来实现滑动窗口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <deque> using namespace std;const int N = 1000010 ;int a[N];int main () int n, k; cin >> n >> k; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i]; deque<int > q; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { while (q.size () && q.back () > a[i]) q.pop_back (); q.push_back (a[i]); if (i - k >= 1 && q.front () == a[i - k]) q.pop_front (); if (i >= k) cout << q.front () <<" " ; } q.clear (); cout << endl; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { while (q.size () && q.back () < a[i]) q.pop_back (); q.push_back (a[i]); if (i - k >= 1 && a[i - k] == q.front ()) q.pop_front (); if (i >= k) cout << q.front () << " " ; } }
831. KMP字符串 感觉这个记了没半小时就忘了ಥ_ಥ
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 , M = 1000010 ;int n, m;int ne[N];char s[M], p[N];int main () cin >> n >> p + 1 >> m >> s + 1 ; for (int i = 2 , j = 0 ; i <= n; i ++ ) { while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1 ]) j = ne[j]; if (p[i] == p[j + 1 ]) j ++ ; ne[i] = j; } for (int i = 1 , j = 0 ; i <= m; i ++ ) { while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1 ]) j = ne[j]; if (s[i] == p[j + 1 ]) j ++ ; if (j == n) { printf ("%d " , i - n); j = ne[j]; } } return 0 ; }
Trie树(前缀树或字典树) 高效存储查找字符串
835. Trie字符串统计 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 ;int son[N][32 ], cnt[N], idx;char str[N];void insert (char * str) int p = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; str[i]; i++){ int u = str[i] - 'a' ; if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx; p = son[p][u]; } cnt[p]++; } int query (char *str) int p = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; str[i]; i++){ int u = str[i] - 'a' ; if (!son[p][u]) return 0 ; p = son[p][u]; } return cnt[p]; } int main () int m; cin >> m; while (m--) { char op[2 ]; scanf ("%s%s" , op, str); if (*op == 'I' ) insert (str); else printf ("%d\n" , query (str)); } return 0 ; }
143. 最大异或对 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 ;int son[N*31 ][2 ], idx,n,a[N];void insert (int x) int p = 0 ; for (int i = 30 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int u = x >> i & 1 ; if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx; p = son[p][u]; } } int query (int x) int p = 0 ,res = 0 ; for (int i = 30 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int u = x >> i & 1 ; if (son[p][!u]) { p = son[p][!u]; res = res * 2 + 1 ; } else { p = son[p][u]; res = res * 2 +0 ; } } return res; } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; insert (a[i]); } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { res = max (res, query (a[i])); } cout << res; return 0 ; }
并查集
将含有两个元素的两个集合合并
询问两个元素是否在一个集合中
优化:路径压缩
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) p[x] =find (p[x]); return p[x]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
acwing 836. 合并集合 cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <iostream> const int N = 100050 ;int n, m;int p[N];int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) p[x] =find (p[x]); return p[x]; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i; while (m--) { char op[2 ]; int a, b; scanf ("%s%d%d" , op, &a, &b); if (op[0 ] == 'M' ) p[find (a)] = find (b); else { if (find (a) == find (b)) puts ("Yes" ); else puts ("No" ); } } }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import sysinput = lambda : sys.stdin.readline().strip()n, m = map (int , input ().split()) p = [i for i in range (n+1 )] size = [1 ] * (n+1 ) def find (x ): while p[x] != x: p[x] = p[p[x]] x = p[x] return p[x] for _ in range (m): op, *args = input ().split() if op == "Q" : a, b = map (int , args) print ("Yes" if find(a) == find(b) else "No" ) elif op == "M" : a, b = map (int , args) root_a = find(a) root_b = find(b) if root_a != root_b: if size[root_a] > size[root_b]: p[root_b] = root_a size[root_a] += size[root_b] else : p[root_a] = root_b size[root_b] += size[root_a]
837. 连通块中点的数量 我们只需要再维持一个点的数量的数组。
cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 1000050 ;int n, m;int p[N], siz[N];int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find (p[x]); return p[x]; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = i; siz[i] = 1 ; } while (m--) { char op[5 ]; scanf ("%s" , op); int a, b; if (op[0 ] == 'C' ) { scanf ("%d%d" , &a, &b); if (find (a) == find (b)) continue ; siz[find (b)] += siz[find (a)]; p[find (a)] = find (b); } else if (op[1 ] == '2' ) { scanf ("%d" , &a); printf ("%d\n" , siz[find (a)]); } else { scanf ("%d%d" , &a, &b); if (find (a) == find (b)) puts ("Yes" ); else puts ("No" ); } } }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import syssys.setrecursionlimit(100000 ) input = lambda : sys.stdin.readline().strip()n, m = map (int , input ().split()) p = [i for i in range (n+1 )] siz = [1 ] * (n+1 ) def find (x ): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) return p[x] for _ in range (m): parts = input ().split() op = parts[0 ] if op == "C" : a, b = map (int , parts[1 :]) root_a = find(a) root_b = find(b) if root_a != root_b: p[root_a] = root_b siz[root_b] += siz[root_a] elif op == "Q1" : a, b = map (int , parts[1 :]) print ("Yes" if find(a) == find(b) else "No" ) elif op == "Q2" : a = int (parts[1 ]) print (siz[find(a)])
240. 食物链
余1可以吃根节点
余2可以被根节点吃
余3与根节点同类
//TODO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 5 * 1e4 + 10 ; int n, m; int p[N], d[N]; int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) { int t = find (p[x]); d[x] += d[p[x]]; p[x] = t; } return p[x]; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = i; } int res = 0 ; while (m--) { int r, x, y; cin >> r >> x >> y; if (x > n || y > n) { res++; } else { int px = find (x), py = find (y); if (r == 1 ) { if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y]) % 3 ) { res++; } else if (px != py) { p[px] = py; d[px] = d[y] - d[x]; } } else if (r == 2 ) { if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y] - 1 ) % 3 ) { res++; } else if (px != py) { p[px] = py; d[px] = d[y] + 1 - d[x]; } } } } cout << res; }
P3958 [NOIP 2017 提高组] 奶酪 这题的关键是识别出这是属于并查集的答案 ,同时注意对于大数据long long类型的比较
思路:
将每个洞虚拟化为并查集集合,并记录连接底部和顶部的洞。
双重循环,遍历合并能连通的洞
判断连接底部和顶部的点是否位于同一集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #include <iostream> #include <utility> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 100001 ; typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int T;int n,h,r;long long point[N][3 ];int toppoint[N], lowpoint[N]; int p[N];int lowcnt = 0 ;int topcnt = 0 ;int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find (p[x]); return p[x]; } bool distin (int i, int j) return 4LL *r*r >= ((point[i][0 ]-point[j][0 ])*(point[i][0 ]-point[j][0 ]) + (point[i][1 ]-point[j][1 ])* (point[i][1 ]-point[j][1 ]) +(point[i][2 ]-point[j][2 ])*(point[i][2 ]-point[j][2 ]) ) ? true : false ; } void solve () lowcnt = 0 ; topcnt = 0 ; cin >> n >> h >> r; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i; for (int i = 1 ; i <=n; i++) { cin >> point[i][0 ] >>point[i][1 ] >> point[i][2 ] ; if (point[i][2 ] - r <= 0 ) lowpoint[lowcnt++] = i; if (point[i][2 ]+r >= h) toppoint[topcnt++] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = i+1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (distin (i,j)) p[find (j)] = find (i); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < topcnt;i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < lowcnt; j++) { if (find (toppoint[i]) == find (lowpoint[j])) { cout << "Yes" << endl; return ; } } } cout << "No" << endl; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cin >> T; while (T--) { solve (); } }
堆
插入一个数
求当前集合最小值
删除最小值
删除或修改任意元素
1为根,左儿子,2x,右儿子2x+1
838. 堆排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std;int n, m, siz;const int N = 100010 ;int h[N];void down (int u) int t = u; if (h[2 * u] < h[t] && 2 * u <= siz) t = 2 * u; if (h[2 * u + 1 ] < h[t] && (2 * u + 1 ) <= siz) t = 2 * u + 1 ; if (t != u) { swap (h[t], h[u]); down (t); } } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) cin >> h[i]; siz = n; for (int i = n / 2 ; i >= 1 ; i--) down (i); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { cout << h[1 ] << " " ; h[1 ] = h[siz--]; down (1 ); } }
839. 模拟堆 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N=1e5 +10 ;int h[N]; int ph[N]; int hp[N]; int cur_size; void heap_swap (int a,int b) swap (h[a],h[b]); swap (hp[a],hp[b]); swap (ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]) ; } void down (int u) int t=u; if (u*2 <=cur_size&&h[t]>h[u*2 ]) t=u*2 ; if (u*2 +1 <=cur_size&&h[t]>h[u*2 +1 ]) t=u*2 +1 ; if (u!=t) { heap_swap (u,t); down (t); } } void up (int u) if (u/2 >0 &&h[u]<h[u/2 ]) { heap_swap (u,u/2 ); up (u>>1 ); } } int main () int n; cin >> n; int m = 0 ; while (n--) { string op; int k,x; cin>>op; if (op=="I" ) { cin>>x; m++; h[++cur_size]=x; ph[m]=cur_size; hp[cur_size]=m; up (cur_size); } else if (op=="PM" ) cout<<h[1 ]<<endl; else if (op=="DM" ) { heap_swap (1 ,cur_size); cur_size--; down (1 ); } else if (op=="D" ) { cin>>k; int u=ph[k]; heap_swap (u,cur_size); cur_size--; up (u); down (u); } else if (op=="C" ) { cin>>k>>x; h[ph[k]]=x; down (ph[k]); up (ph[k]); } } return 0 ; }
//TODO
哈希表 840. 模拟散列表 拉链法: 数组 +(重复元素插入链表)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100003 ;int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;void insert (int x) int k = (x % N + N) % N; e[idx] = x; ne[idx] = h[k]; h[k] = idx++; } bool find (int x) int pos = (x % N + N) % N; for (int i = h[pos]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) { if (x == e[i]) return true ; } return false ; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof (h)); int n; scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { char op[2 ]; int x; scanf ("%s%d" , op, &x); if (op[0 ] == 'I' ) insert (x); else if (op[0 ] == 'Q' ) { if (find (x)) printf ("Yes\n" ); else printf ("No\n" ); } } }
开放寻址法 N应该取题目要求的两到三倍
1 2 3 4 (x % N + N) % N; 第一个x % N可能得到负数(如果x为负) + N确保结果为正 第二个% N确保结果在正确范围内
cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 200003 , null = 0x3f3f3f3f ; int h[N];int find (int x) int pos = (x % N + N) % N; while (h[pos] != null && h[pos] != x) { pos++; if (pos == N) pos = 0 ; } return pos; } int main () memset (h, 0x3f , sizeof (h)); int n; scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { char op[2 ]; int x; scanf ("%s%d" , op, &x); if (op[0 ] == 'I' ) h[find (x)] = x; else if (op[0 ] == 'Q' ) { if (h[find (x)] != null) printf ("Yes\n" ); else printf ("No\n" ); } } }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 n = int (input ()) null = 0x3f3f3f3f arr = [null]*n*3 def find (x ): pos = (x%n+n)%n while arr[pos] !=null and arr[pos] != x: pos = pos+1 if pos == n: pos = 0 return pos for i in range (n): op, x = input ().split() x = int (x) if op == 'I' : arr[find(x)] = x else : pos = find(x) if arr[pos] != null: print ('Yes' ) else : print ('No' )
AcWing 841. 字符串哈希(字符串前缀哈希法) AcWing 841. 字符串哈希 【公式助理解】 - AcWing
cpp P = 13331,Q=2^64
创建方程
h[i] = [h[i-1]*P+ ord(arr[i-1])] %mod, 创建哈希 (注意下标,防止查询时数组越界)
p[i] = p[i]P % mod p` `i次方
查询方程h[r] - h[l-1] * p[r-l+1] l-1>=0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;typedef unsigned long long ULL;const int N = 1e5 +5 ,P = 13331 ;ULL h[N],p[N]; ULL query (int l,int r) { return h[r] - h[l - 1 ]*p[r - l + 1 ]; } int main () int n, m; cin >> n >> m; string s; cin >> s; p[0 ] = 1 ; h[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i =0 ; i < s.size (); i++) { h[i + 1 ] = h[i] * P + s[i]; p[i + 1 ] = p[i] * P; } while (m--) { int l1, l2, r1, r2; cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2; if (query (l1, r1) == query (l2, r2)) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl; } }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 n,m = map (int ,input ().split()) mod = 10 **9 +7 P = 13331 h = [0 ]*(n+10 ) p = [1 ]*(n+10 ) def query (l,r ): return (h[r] - h[l-1 ]*p[r-l+1 ])%mod s = input () for i in range (1 ,n+1 ): p[i] = (p[i-1 ]*P) % mod h[i] = (h[i-1 ]*P + ord (s[i-1 ])) % mod for _ in range (m): l1,r1,l2,r2 = map (int ,input ().split()) if query(l1,r1) == query(l2,r2): print ('Yes' ) else : print ('No' )