[toc]
基础课 图的存储 cpp 链式前向星
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;void add (int a,int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx ++; }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 graph = {} n = int (input ().strip()) for i in range (n-1 ): a, b = map (int , input ().split()) if a not in graph: graph[a] = [b] else : graph[a].append(b) if b not in graph: graph[b] = [a] else : graph[b].append(a) st = [False for i in range (n+1 )] def dfs (u ): st[u] = True for i in range (graph[u]): if not st[i]: dfs(i)
数据结构
空间
DFS
stack
O(n)
BFS
queue
最短路
算法 优点 缺点 适用问题
DFS 空间效率高,适合深层遍历
不保证最短路径,可能栈溢出
路径搜索、回溯、拓扑排序
BFS 保证最短路径,适合层次遍历
空间占用大(存储整层节点)
最短路径、扩散问题、层次分析
DFS
采用stack
回溯——恢复状态
剪枝——提前回溯
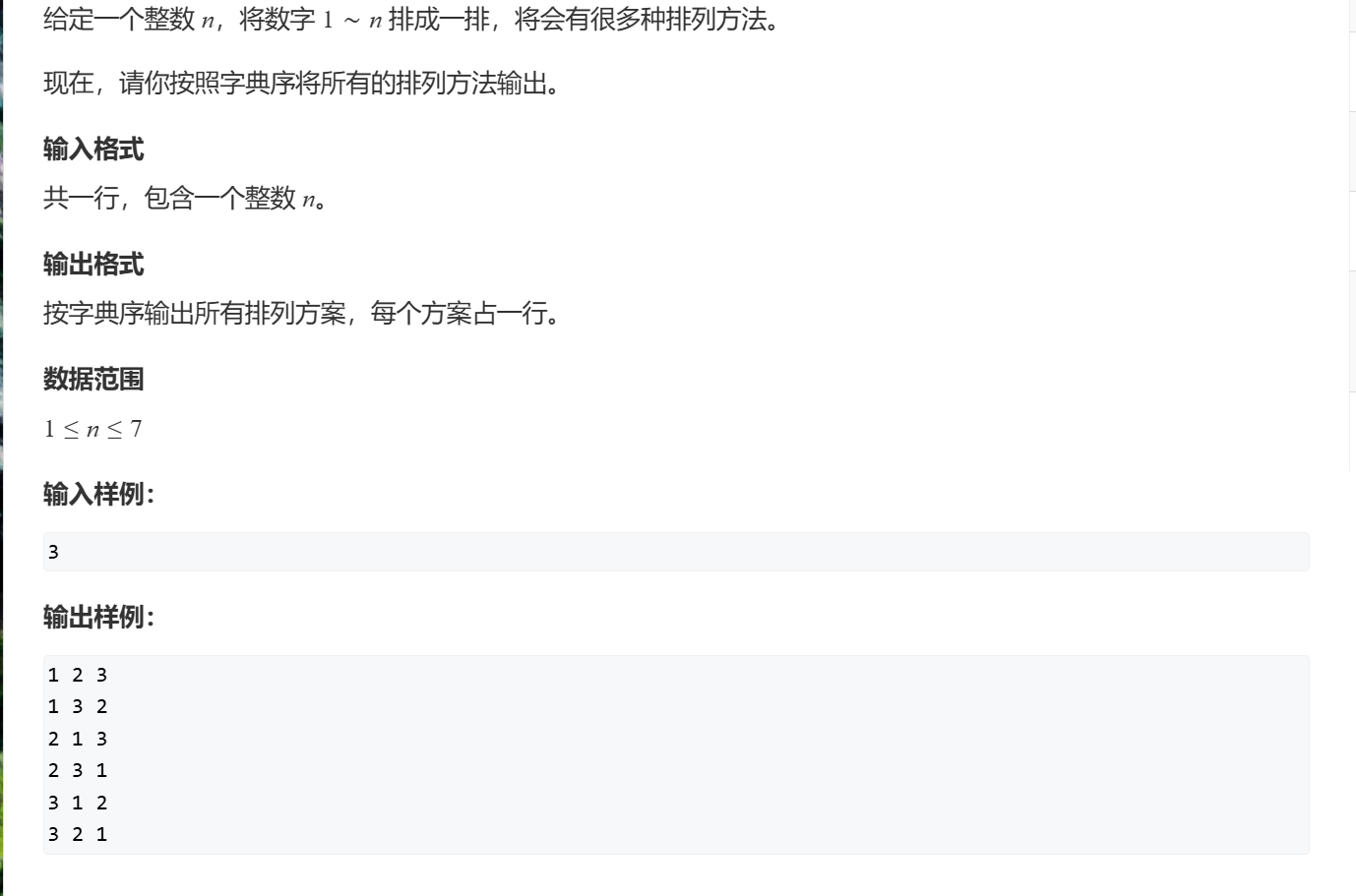
遇到诸如放置、字典序等可使用深搜输出全部组合。
AcWing 842. 排列数字 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <iostream> using namespace std ; const int N = 100 ;int n; int path[N];int st[N];void dfs (int u) { if (u== n) { for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i ++) printf ("%d" , path[i]); puts ("" ); return ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++) { if (!st[i]) path[u] = i; st[i] = true ; dfs(u + 1 ); st[i] = false ; } } int main () { cin >> n; dfs(0 ); return 0 ; }
AcWing 843. n-皇后问题 通过枚举每行(若n皇后问题能解决,则每行必有一个皇后),再通过行列表示主对角线和副对角线,判断条件符合则递归调用dfs。
所有主对角线上的点 ,其坐标差 i −j 相同。(x+1)-(y+1) = x-y所有副对角线上的点 ,其坐标和 i +j 相同。(x-1)-(y-1) = x+y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 200 ; int n;char g[N][N];bool col[N], dg[N], udg[N];void dfs (int u) if (u == n) { for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i ++) puts (g[i]); puts ("" ); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) { if (!col[i] && !dg[u + i] && !udg[n - u + i]) { g[u][i] = 'Q' ; col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = true ; dfs (u + 1 ); col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = false ; g[u][i] = '.' ; } } } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++) g[i][j] = '.' ; dfs (0 ); return 0 ; }
BFS
采用queue
边权都为1时,为最短路径
DP是特殊的最短路问题
AcWing 844. 走迷宫 BFS算法相当于在有m个后继点的点处分裂为m个小鼠,同时将访问过的点在数组上标定距离(该距离是最小值,因为其他点在相同步数下并不能访问该点),最后返回要求的坐标即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <iostream> #include <utility> #include <queue> using namespace std ; typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e2 +10 ; int arr[N][N];int d[N][N]; int n,m;typedef pair <int ,int > PA;typedef pair <int ,PA> PA2 ;int xway[] = {-1 ,0 ,0 ,1 };int yway[] = {0 ,-1 ,1 ,0 };void bfs (int x, int y) { queue <PA> qu; qu.push({x,y}); while (!qu.empty()) { auto tmp = qu.front(); qu.pop(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int xx = tmp.first + xway[i]; int yy = tmp.second + yway[i]; if (xx > 0 && xx <= n && yy > 0 && yy <= m && arr[xx][yy]!= 1 && d[xx][yy]==0 ) { d[xx][yy] = d[tmp.first][tmp.second] + 1 ; qu.push({xx,yy}); } } } } int main () { cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) cin >> arr[i][j]; bfs(1 ,1 ); cout << d[n][m] << endl ; }
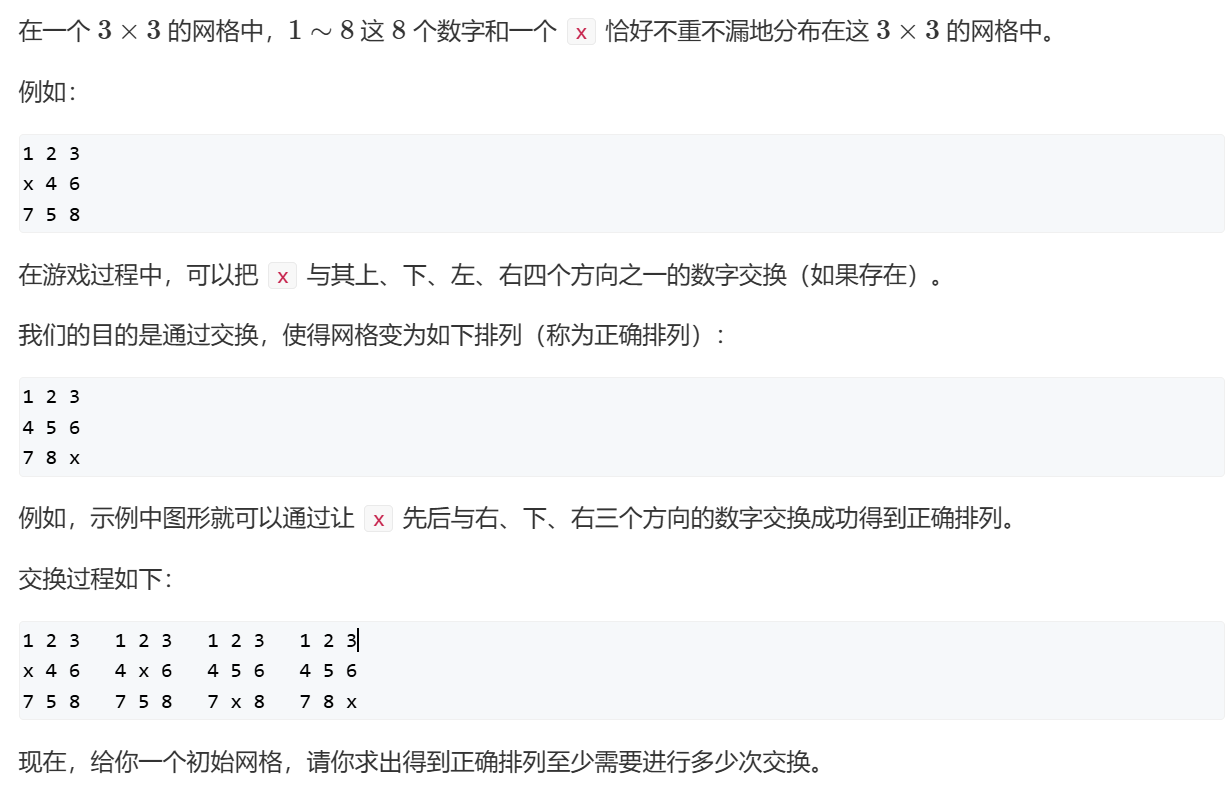
AcWing 845. 八数码 字符串上BFS这题我们从输入的状态出发,直到到达最终的状态,本质是bfs算法,通过枚举所有可能的变换,在变换的基础上再进行枚举,直到匹配最终状态。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 记录一个错误的方向数组 int way[] = {-3,+3,-1,1}; 1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8 若取x+way[2],则swap(x,3)不符合题意 因此对于该题,应该先转化为x,y的
通过<unordered_map>存储该状态的最短路径
若.count()存在,说明已经访问过且当前路径不是最短路径
若!.count(),则说明未访问该路径,添加到map
为什么使用<unordered_map>
能保证O(1)的访问时间,但是不能进行排序 <map>访问时间为(logn),按键自动排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std;string finnal = "12345678x" ; unordered_map<string, int > un_map; queue<string> status; int bfs (string st) un_map[st] = 0 ; status.push (st); int xway[4 ] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int yway[4 ] = {0 , -1 , 0 , 1 }; while (status.size ()) { string tmp = status.front (); status.pop (); int pos = tmp.find ('x' ); int x = pos / 3 ; int y = pos % 3 ; int distance = un_map[tmp]; if (tmp == finnal) return distance; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int a = x + xway[i], b = y + yway[i]; if (a >= 0 && a < 3 && b >= 0 && b < 3 ) { swap (tmp[pos], tmp[3 * a + b]); if (!un_map.count (tmp)) { un_map[tmp] = distance + 1 ; status.push (tmp); } swap (tmp[pos], tmp[3 * a + b]); } } } return -1 ; } int main () string st; for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++) { char tmp; cin >> tmp; st += tmp; } cout << bfs (st) << endl; return 0 ; }
树与图的深度优先遍历 acwing846 树的重心 cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 , M = N * 2 ;int n;int ans = N;int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;bool st[N]; ·void add (int a,int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx ++; } int dfs (int u) st[u] = true ; int sum = 1 ; int res = 0 ; for (int i = h[u]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (!st[j]) { int s = dfs (j); res = max (res, s); sum += s; } } res = max (res, n - sum); ans = min (ans, res); return sum; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); int a,b; cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ;i < n ; i ++) { cin >> a >>b; add (a, b), add (b, a); } dfs (1 ); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 n = int (input ().strip()) st = [False for _ in range (n+1 )] graph = {} res = n def dfs (u ): global res st[u] = True size = 0 sumNode = 0 for v in graph[u]: if not st[v]: s = dfs(v) sumNode = sumNode+ s size = max (size, s) size = max (size, n-sumNode-1 ) res = min (res, size) return sumNode+1 for _ in range (n-1 ): a, b = map (int , input ().split()) if a not in graph: graph[a] = [b] else : graph[a].append(b) if b not in graph: graph[b] = [a] else : graph[b].append(a) dfs(3 ) print (res)
树与图的广度优先遍历 AcWing 847. 图中点的层次 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> using namespace std;typedef pair<int ,int > PII;const int N = 100010 ;int h[N],ne[N],e[N],idx,st[N];int dist[N];int n,m;int add (int a,int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } void bfs () memset (dist,0x3f3f3f3f ,sizeof dist); dist[1 ] = 0 ; st[1 ] = 1 ; queue<int > q; q.push (1 ); while (!q.empty ()) { int t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = h[t];i!=-1 ;i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (!st[j]) { st[j] = 1 ; dist[j] = dist[t]+1 ; q.push (j); } } } } int main () memset (h,-1 ,sizeof h); cin>>n>>m; for (int i = 0 ;i<m;i++) { int a,b; cin>>a>>b; add (a,b); } bfs (); if (dist[n]==0x3f3f3f3f ) cout<<-1 ; else cout<<dist[n]; return 0 ; }
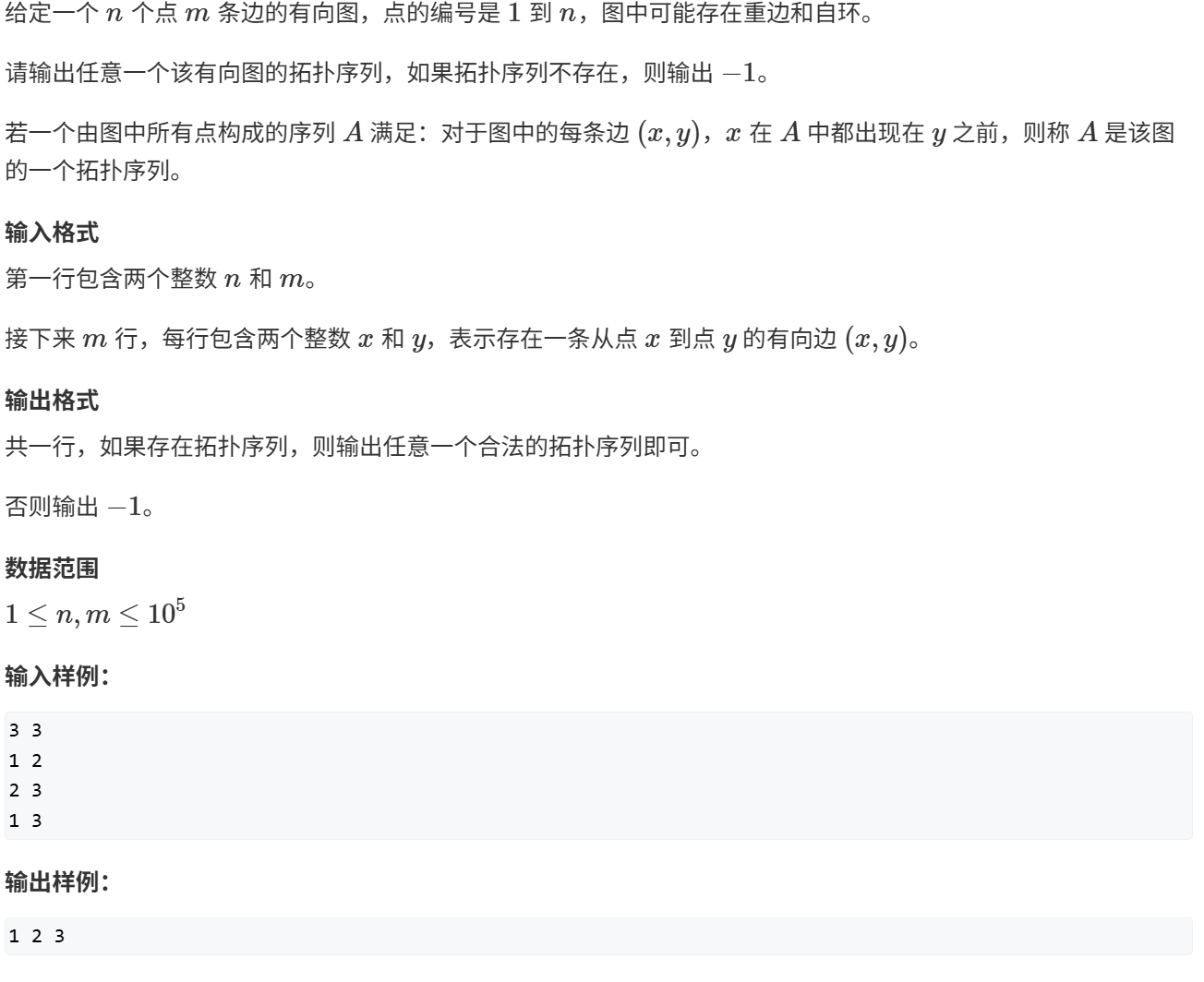
拓扑序列(有向图)
统计所有节点的入度 (指向该节点的边数)。
将入度为 0 的节点加入队列。
依次取出队列中的节点,并“删除”它(将其邻接节点的入度减 1)。
若邻接节点入度变为 0,则加入队列。
重复直到队列为空。若所有节点被处理,则得到拓扑序列;否则图中存在环。
AcWing 848. 有向图的拓扑序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <utility> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e5 +10 ; int arr[N];typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int n,m;int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx ;int q[N], d[N];int hh = 0 ,tt = -1 ;void add (int a, int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx ++; } void topsort () for (int i = 1 ; i<=n;i++) { if (!d[i]) q[++tt] = i; } while (hh<=tt) { int p = q[hh++]; for (int i = h[p];i!=-1 ; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; d[j] --; if (d[j] == 0 ) { q[++tt] = j; } } } return ; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cin >> n >> m; memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); for (int i = 0 ; i< m; i++) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; add (a,b); d[b]++; } topsort (); if (tt == n-1 ) for (int i = 0 ; i< n;i++) { cout << q[i] <<" " ; } else cout << -1 << endl; return 0 ; }
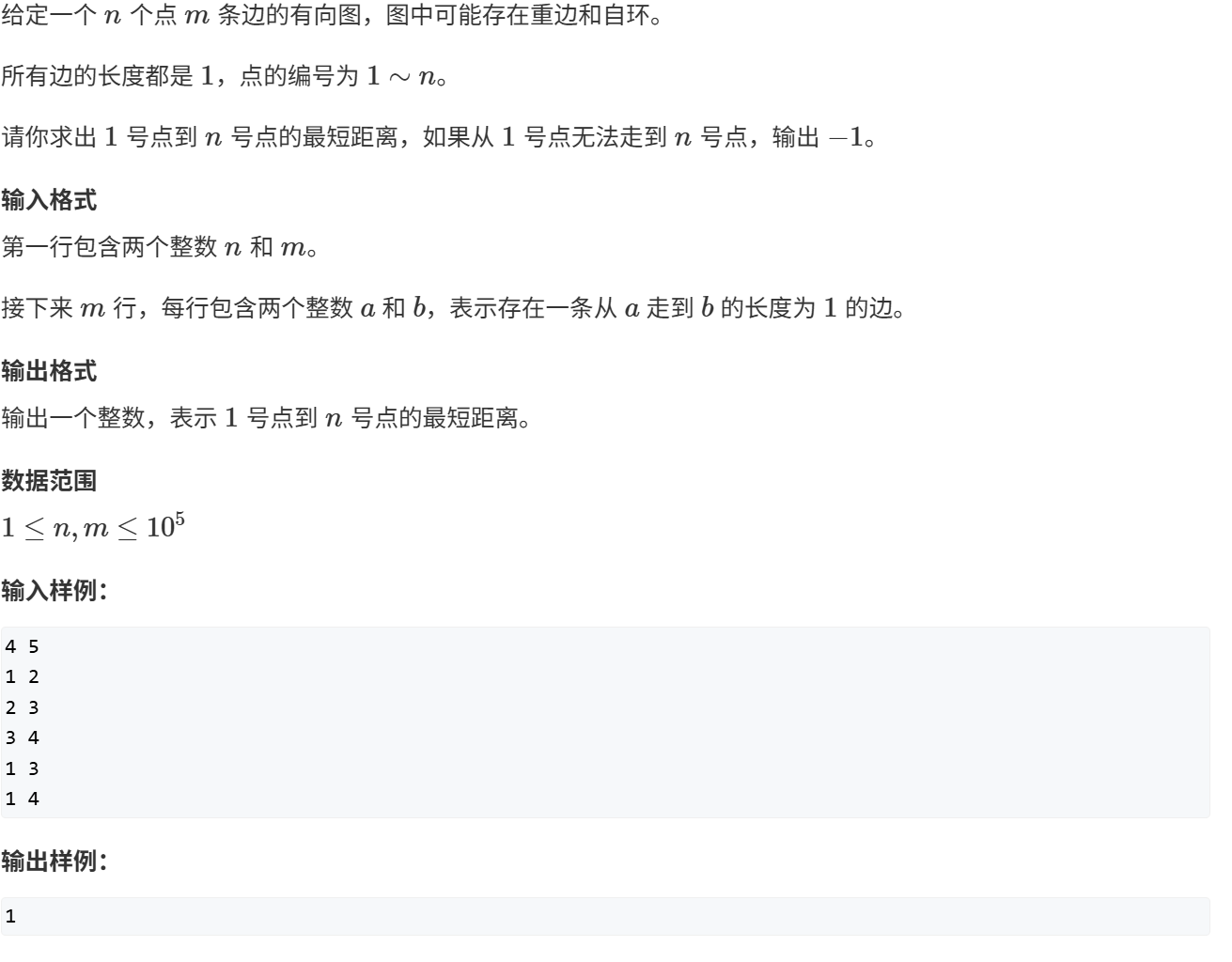
最短路问题 单源最短路 Dijkstra是用最短的边去更新其他边,而spfa是上次更新的终点去更新其他边,Bellman-Ford则暴力每次更新所有边
所有边权都为正数
算法
时间复杂度
适用场景
核心思想
朴素Dijkstra O(n²)
稠密图
每次选择当前距离起点最近的未确定节点,贪心扩展。
堆优化Dijkstra O(mlogn)
稀疏图
用优先队列维护未确定节点的最小距离,避免线性扫描。
存在负权边
算法
时间复杂度
适用场景
核心思想
Bellman-Ford O(nm)
任意图
对所有边进行松弛操作,重复 n-1 次保证收敛。
SPFA 平均 O(m),最坏 O(nm)
负权图但无负环(负环权值之和为负数)
队列优化 Bellman-Ford,仅松弛距离被更新的节点。
多源汇点最短路 Floyd算法 O()
动态规划:逐步允许通过中间节点 k 更新任意两点间的最短距离。
不能处理负环
Dijkstra AcWing 849. Dijkstra求最短路 I 朴素Dijkstra算法
将除起点外的距离都置为无穷
选取当前点到另一未访问且距离最短的边
更新所有点到起点的距离
重复2——3,直到到达终点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 510 ;int g[N][N]; int dist[N]; bool st[N]; int n, m;int Dijkstra () memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); dist[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int t = -1 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) t = j; } st[t] = true ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { dist[j] = min (dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]); } } if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) return -1 ; return dist[n]; } int main () cin >> n >> m; memset (g, 0x3f , sizeof g); while (m--) { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; g[a][b] = min (g[a][b], c); } cout << Dijkstra () << endl; return 0 ; }
AcWing 850. Dijkstra求最短路 II 使用优先队列模拟堆来实现距离的排序,同时再出队时遍历从该点出发的边实现更新最短距离值。
cpp
使用小根堆(priority_queue)快速获取当前未处理节点中距离最小的节点。
相较于朴素版dijkstra算法,堆优化版通过邻接表遍历自动覆盖来处理重边,自环若权值为正则不影响结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 150010 ;int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;int w[N]; int dist[N];bool st[N];int n, m;void add (int a, int b, int c) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; w[idx] = c; h[a] = idx++; } int dijkstra () memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); dist[1 ] = 0 ; priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap; heap.push ({0 , 1 }); while (heap.size ()) { auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); int distance = t.first, node = t.second; if (st[node]) continue ; st[node] = true ; for (int i = h[node]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (dist[j] > dist[node] + w[i]) { dist[j] = dist[node] + w[i]; heap.push ({dist[j], j}); } } } if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) return -1 ; else return dist[n]; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof (h)); scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); while (m--) { int x, y, c; scanf ("%d%d%d" , &x, &y, &c); add (x, y, c); } cout << dijkstra () << endl; return 0 ; }
python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import osimport heapqimport sysimport mathsys.setrecursionlimit(10000 ) input = lambda : sys.stdin.readline().strip()n,m = map (int ,input ().split()) graph = {i: [] for i in range (1 ,n+10 )} inf = float (math.inf) dist = [inf] * (n+10 ) st = [False ] * (n+10 ) def dij (): hp = [] heapq.heappush(hp,[0 ,1 ]) while hp: dis, point = heapq.heappop(hp) if st[point]: continue st[point] = True for v,w in graph[point]: if dist[v] > dis + w: dist[v] = dis + w heapq.heappush(hp,(dist[v],v)) for i in range (m): x,y,z = map (int ,input ().split()) graph[x].append((y,z)) dij() if dist[n] == inf: print (-1 ) else : print (dist[n])
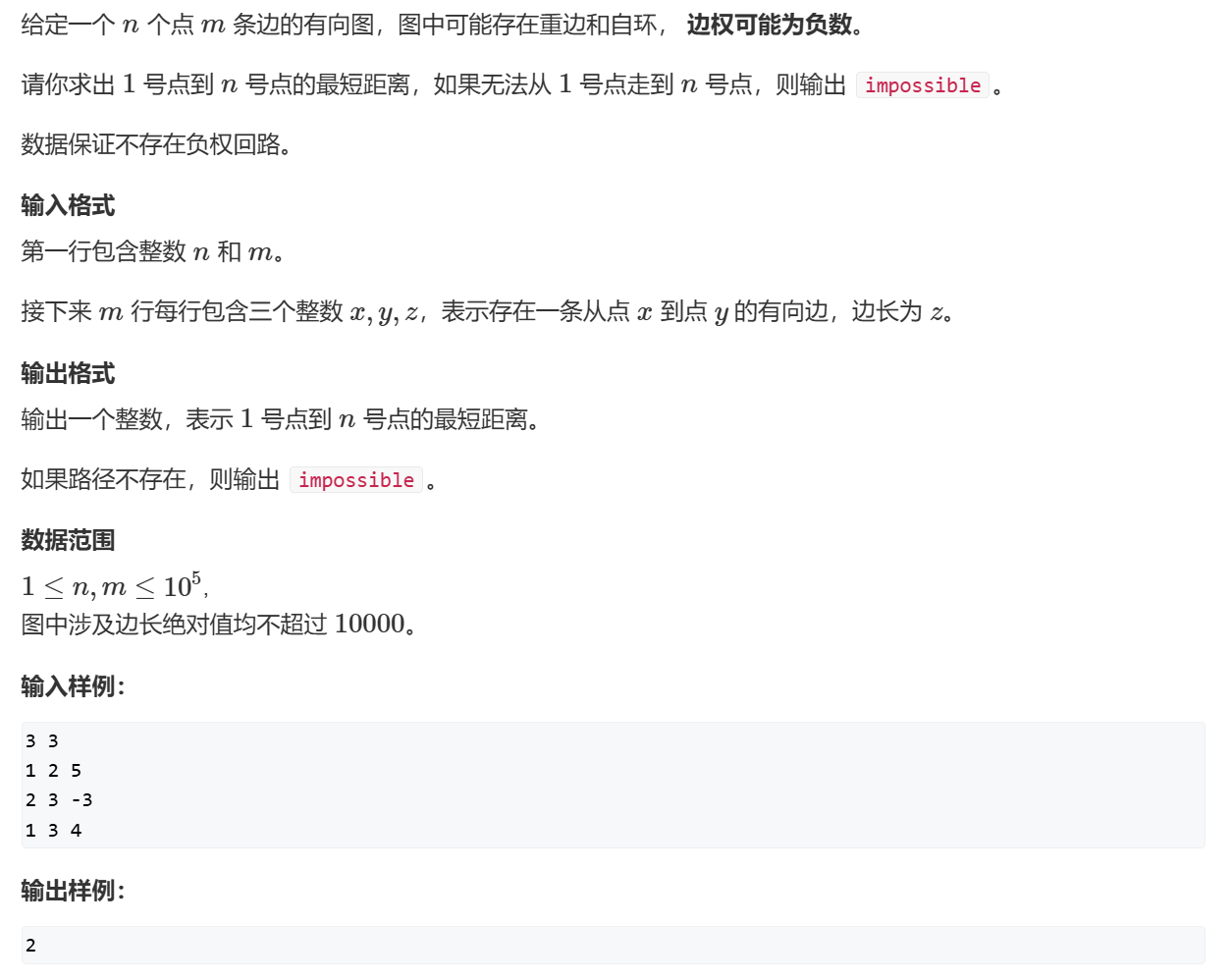
bellman-ford (有边数限制) AcWing 853. 有边数限制的最短路 连续进行松弛,在每次松弛时把每条边都更新一下。
若在 n-1 次松弛后还能更新,则说明图中有负环,因此无法得出结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N = 510 , M = 10010 ;struct Edge { int a; int b; int w; } e[M]; int dist[N];int back[N];int n, m, k;void bellman_ford () memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); dist[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { memcpy (back, dist, sizeof dist); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int a = e[i].a, b = e[i].b, w = e[i].w; dist[b] = min (dist[b], back[a] + w); } } } int main () scanf ("%d%d%d" , &n, &m, &k); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int a, b, w; scanf ("%d%d%d" , &a, &b, &w); e[i] = {a, b, w}; } bellman_ford (); if (dist[n]>0x3f3f3f3f /2 ) puts ("impossible" ); else printf ("%d" ,dist[n]); return 0 ; }
spfa AcWing 851. spfa求最短路
只有当一个点的前驱结点更新了,该节点才会得到更新 —>创建一个队列每一次加入距离被更新的结点。
st数组的作用:判断当前的点是否已经加入到队列中,减少不必要的遍历
有负权回路SPFA会死循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 ;int n, m;int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;int dist[N];bool st[N]; void add (int a, int b, int c) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; w[idx] = c; h[a] = idx++; } int spfa () memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); queue<int > q; q.push (1 ); dist[1 ] = 0 ; while (q.size ()) { int t = q.front (); q.pop (); st[t] = false ; for (int i = h[t]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]) { dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i]; if (!st[j]) { st[j] = true ; q.push (j); } } } } return dist[n]; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ int a, b, w; cin >> a >> b >> w; add (a, b, w); } spfa (); if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) cout << "impossible" ; else cout << dist[n]; return 0 ; }
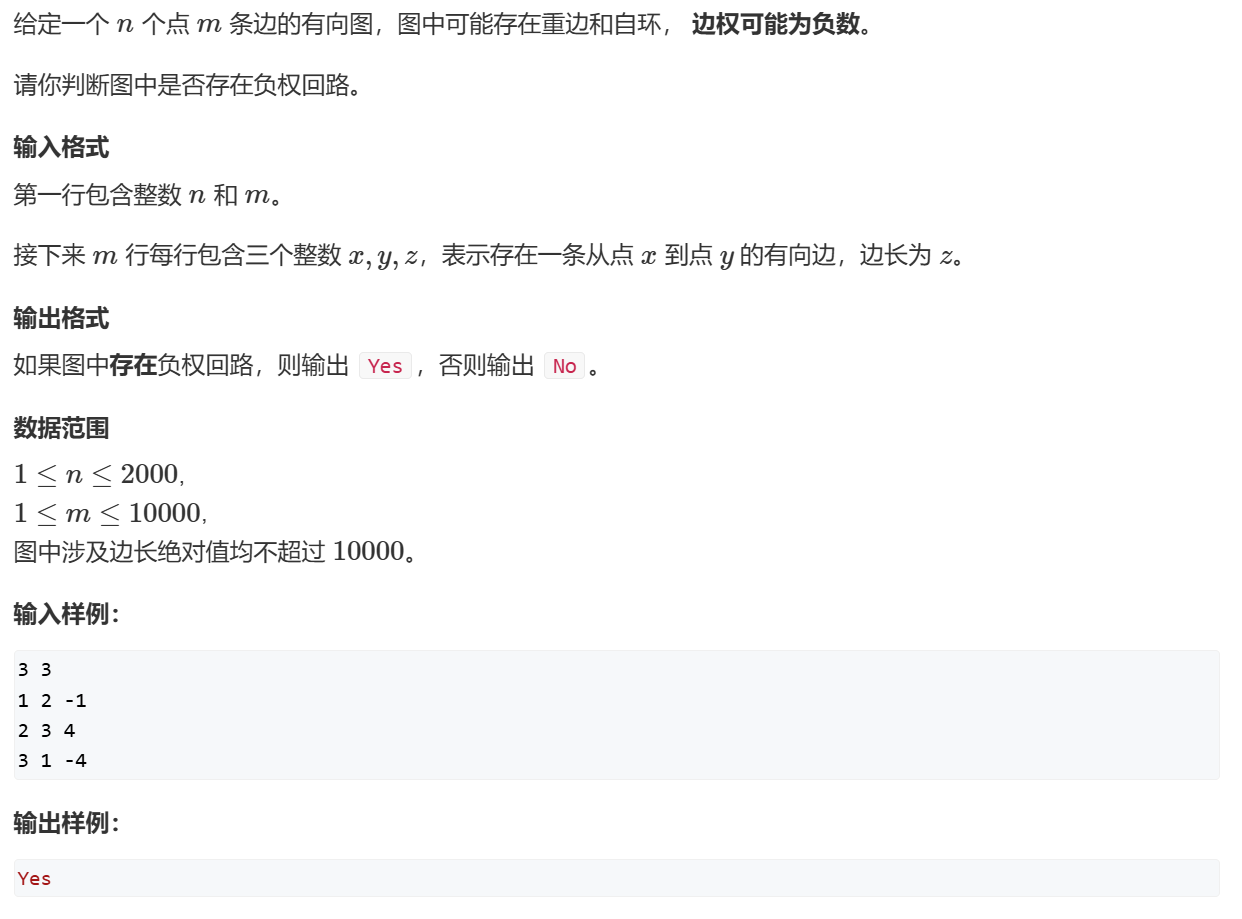
AcWing 852. spfa判断负环 统计当前每个点的最短路中所包含的边数,如果某点的最短路所包含的边数大于等于n,则也说明存在环
spfa 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;const int N = 2e3 + 10 , M = 1e4 + 10 ;int n, m;int h[N], e[M], ne[M], w[M], idx;bool st[N]; int dist[N]; int cnt[N]; void add (int a, int b, int c) e[idx] = b; w[idx] = c; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } bool spfa () queue<int > q; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { q.push (i); st[i] = true ; } while (!q.empty ()) { int t = q.front (); q.pop (); st[t] = false ; for (int i = h[t]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]) { dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i]; cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1 ; if (cnt[j] >= n) return true ; if (!st[j]) { q.push (j); st[j] = true ; } } } } return false ; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; add (a, b, c); } if (spfa ()) cout << "Yes" ; else cout << "No" ; return 0 ; }
bellman-ford 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 2005 ,M = 1e4 + 5 ,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;struct edge { int a,b,c; }e[M]; int n,m,dis[N];string bellman () memset (dis,0x3f ,sizeof dis); dis[1 ] = 0 ; bool flag = true ; int cnt = 0 ; while (flag) { flag = false ; cnt++; if (cnt > n) return "Yes" ; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++) { int a = e[i].a,b = e[i].b,c = e[i].c; if (dis[b] > dis[a] + c) { flag = true ; dis[b] = dis[a] + c; } } } return "No" ; } int main () cin>>n>>m; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++) { int a,b,c; cin>>a>>b>>c; e[i] = {a,b,c}; } cout<<bellman ()<<endl; return 0 ; }
floyd Floyd-Warshall 算法的动态规划状态转移方程可以表示为:
:允许使用前 k 个节点作为中转时,节点 i 到 j 的最短距离。
状态转移:
滚动数组优化:
d[i][j] ← min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j])
AcWing 854. Floyd求最短路 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <iostream> #include <utility> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e4 +10 ; int d[N][N];int INF = 1e9 ;typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int n,m,Q;void floyd () for (int k = 1 ; k <= n; k++) for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) d[i][j] = min (d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]); } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cin >> n >> m >> Q; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) if (i == j) d[i][j] = 0 ; else d[i][j] = INF; while (m--) { int a,b,c; cin >> a >> b >> c; d[a][b] = min (d[a][b], c); } floyd (); while (Q--) { int a,b; cin >> a >> b; if (d[a][b] > INF/2 ) cout << "impossible" << endl; else cout << d[a][b] << endl; } }
最小生成树
普利姆算法(Prim)
朴素版Prim O(n^2) 稠密图
堆优化版Prim O(mlogn)
克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal) O(mlogm) 稀疏图
Prim AcWing858. Prim算法求最小生成树 Prim算法:我们从其中一个点出发,遍历该点所有边,找到最小权值的边,然后加入集合,更新该边另一顶点引出的边(使从该边引出的节点可达)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 510 , INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;int n, m;int g[N][N];int dist[N];bool st[N]; int prim () memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) { int t = -1 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j ++ ) if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) t = j; if (i && dist[t] == INF) return INF; if (i) res += dist[t]; st[t] = true ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j ++ ) dist[j] = min (dist[j], g[t][j]); } return res; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); memset (g, 0x3f , sizeof g); while (m -- ) { int a, b, c; scanf ("%d%d%d" , &a, &b, &c); g[a][b] = g[b][a] = min (g[a][b], c); } int t = prim (); if (t == INF) puts ("impossible" ); else printf ("%d\n" , t); return 0 ; }
AcWing 858. Prim算法求最小生成树:图解+详细代码注释(带上了保存路径) - AcWing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 510 ;int g[N][N];int dt[N];int st[N];int pre[N];int n, m;void prim () memset (dt,0x3f , sizeof (dt)); int res= 0 ; dt[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int t = -1 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dt[j] < dt[t])) t = j; } if (dt[t] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) { cout << "impossible" ; return ; } st[t] = 1 ; res += dt[t]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (dt[i] > g[t][i] && !st[i]) { dt[i] = g[t][i]; pre[i] = t; } } } cout << res; } void getPath () for (int i = n; i > 1 ; i--) { cout << i <<" " << pre[i] << " " << endl; } } int main () memset (g, 0x3f , sizeof (g)); cin >> n >> m; while (m --) { int a, b, w; cin >> a >> b >> w; g[a][b] = g[b][a] = min (g[a][b],w); } prim (); return 0 ; } 作者:Hasity 链接:https: 来源:AcWing 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
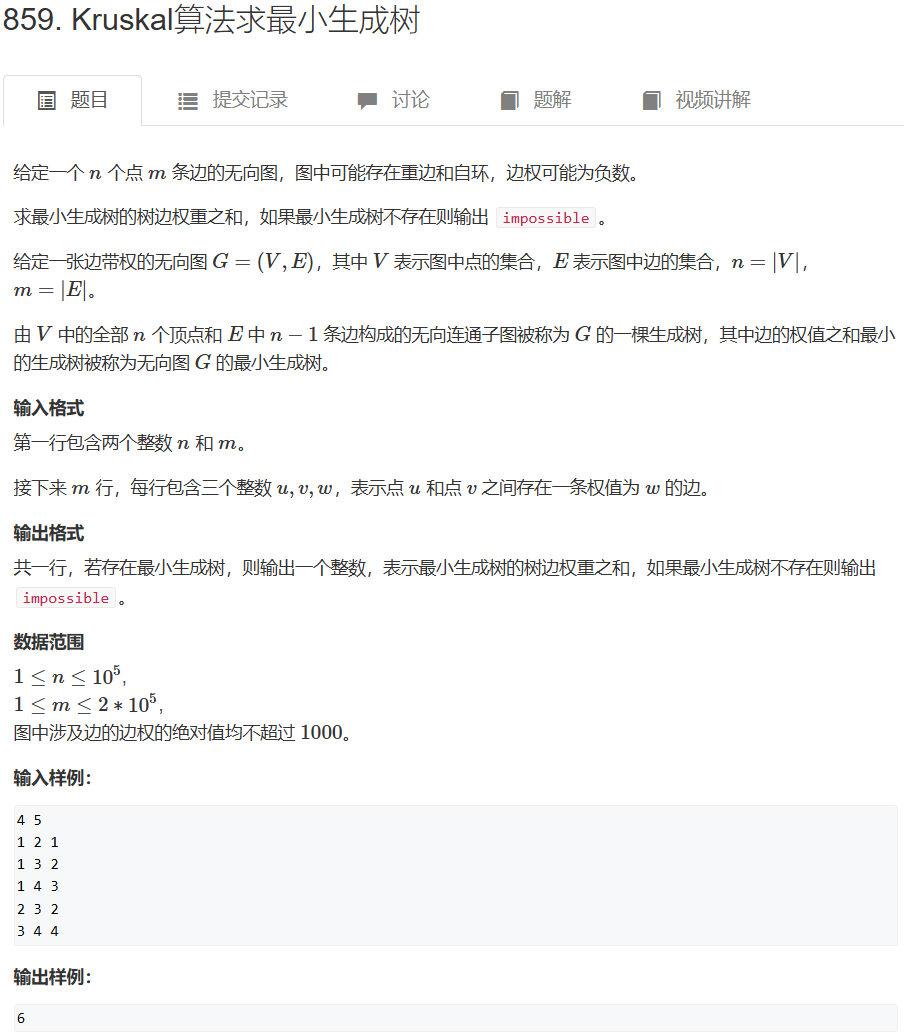
AcWing 859. Kruskal算法求最小生成树 kruskal算法:
通过并查集对边进行合并。先按照从小到大的权重进行排序,然后对每两个未连接的节点进行连边。我们知道,对于一个无向图,每两点有且仅有一条边相连,若其边数小于n-1,则其不联通,不能构成最小生成树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 , M = 200010 , INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;int n, m;int p[N];struct Edge { int a, b, w; bool operator <(const Edge &E) const { return w < E.w; } } edges[M]; int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find (p[x]); return p[x]; } int kruskal () sort (edges, edges + m); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i; int res = 0 , cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i ++ ) { int a = edges[i].a, b = edges[i].b, w = edges[i].w; a = find (a), b = find (b); if (a != b) { p[a] = b; res += w; cnt ++ ; } } if (cnt < n - 1 ) return INF; else return res; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i ++ ) { int a, b, w; scanf ("%d%d%d" , &a, &b, &w); edges[i] = {a, b, w}; } int t = kruskal (); if (t == INF) puts ("impossible" ); else printf ("%d\n" , t); return 0 ; }
二分图
染色法 O(n+m)
匈牙利算法 O(mn),实际运行时间很小
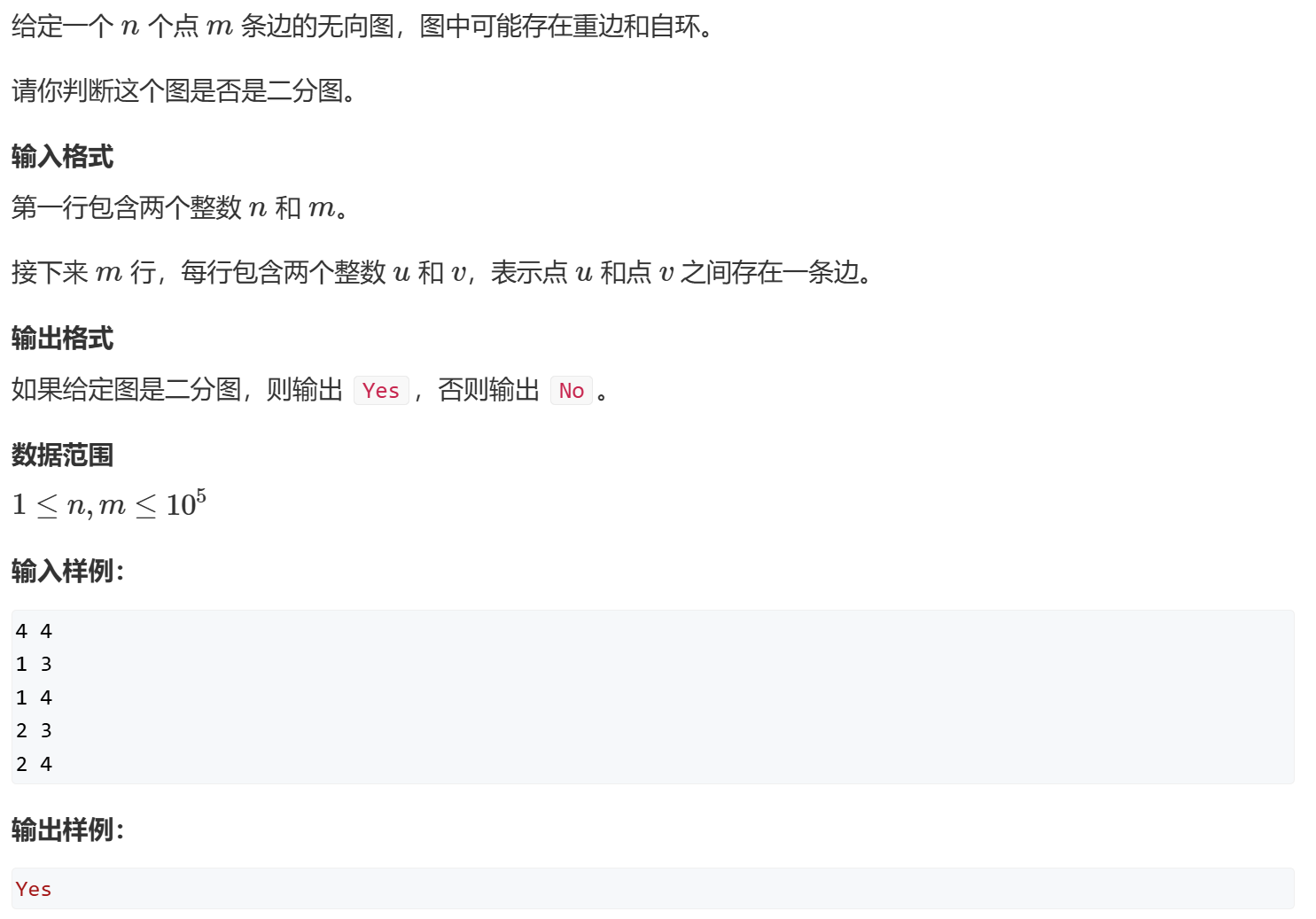
二分图 :二分图是一种特殊的图,其顶点集可以分成两个互不相交的子集,使得每一条边的两个端点分别属于不同的子集。(集合内部没有边)二部 :如果一个图是二分图,那么它没有奇数长度的环。着色 :一个图是二分图当且仅当它可以被 2着色,即可以使用两种颜色对图的顶点进行着色,使得每条边的两个端点的颜色不同。
染色法 AcWing 860. 染色法判定二分图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 * 2 ;int e[N], ne[N], idx;int h[N];int color[N];int n, m;void add (int a,int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } bool dfs (int u, int c) color[u] = c; for (int i = h[u]; i!= -1 ; i = ne[i]) { int b = e[i]; if (!color[b]) { if (!dfs (b, 3 - c)) return false ; } else if (color[b] == c) { return false ; } } return true ; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 0 ;i < m; i ++) { int a, b; scanf ("%d%d" , &a, &b); add (a, b); add (b, a); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (!color[i]) { if (!dfs (i, 1 )) { cout << "No" << endl; return 0 ; } } } cout << "Yes" << endl; return 0 ; }
匈牙利算法: 匈牙利算法是一种用于解决指派问题(Assignment Problem)的数学算法。指派问题是指在有限的候选者中选择一组匹配,使得总的成本最小(或收益最大)。
AcWing 861. 二分图的最大匹配 find(int u): 尝试为左边节点 u 找到一个匹配,使用递归方式实现深度优先搜索(DFS)。
如果右边节点 j 未被访问过,则标记为已访问。
如果右边节点 j 未匹配或者其匹配的左边节点可以重新匹配,则更新匹配关系并返回 true。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N = 505 , M = 1e5 + 10 ;int n1,n2, m;int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;int match[N], st[N]; void add (int a, int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } int find (int u) for (int i = h[u]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]){ int j = e[i]; if (!st[j]){ st[j] = true ; if (match[j] == 0 || find (match[j])){ match[j] = u; return true ; } } } return false ; } int main () memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); scanf ("%d%d%d" , &n1, &n2, &m); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ int a, b; scanf ("%d%d" , &a, &b); add (a, b); } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n1; i++){ memset (st, 0 , sizeof st); if (find (i)) res++; } cout << res; return 0 ; }
提高课
普通 BFS :从单个起点出发,逐层扩展。多源 BFS :从多个起点同时出发,逐层扩展。
取一虚拟原点,将所有起点以边权为0连接到虚拟原点,则转化为单源BFS
多源BFS AcWing 173. 矩阵距离 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <utility> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e3 +10 ; int arr[N];char g[N][N];int d[N][N];typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int n,m;int xway[4 ] = {-1 , 1 , 0 , 0 };int yway[4 ] = {0 , 0 , -1 , 1 };void bfs () queue<pair<int , int >> qu; memset (d, -1 , sizeof d); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) { if (g[i][j] == '1' ) { qu.push ({i, j}); d[i][j] = 0 ; } } while (!qu.empty ()) { auto t = qu.front (); qu.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int x = t.first + xway[i]; int y = t.second + yway[i]; if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && d[x][y] == -1 ) { d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1 ; qu.push ({x, y}); } } } } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) cin>>g[i]; bfs (); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) { cout << d[i][j] << ' ' ; } cout << "\n" ; } }
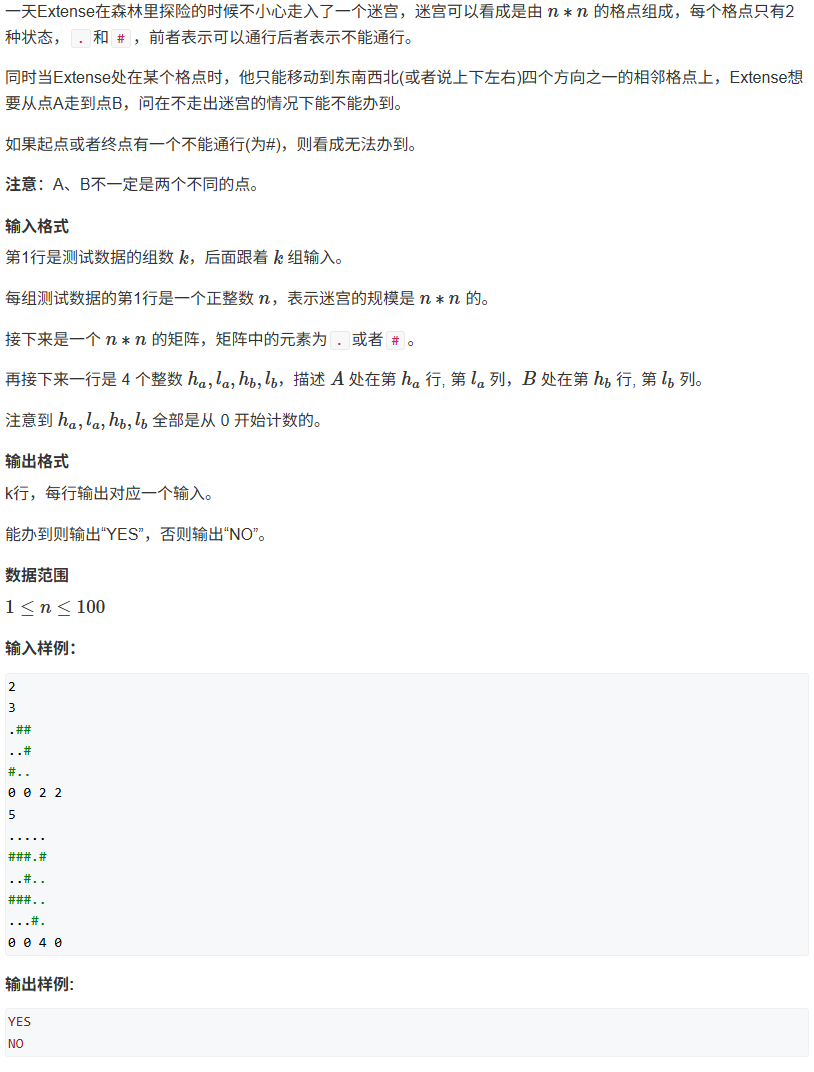
DFS之连通性模型 AcWing 1112. 迷宫 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <iostream> #include <utility> #include <cstring> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e3 +10 ; bool d[N][N];bool st[N][N];typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int n,m;int xway[4 ] = {-1 , 1 , 0 , 0 };int yway[4 ] = {0 , 0 , -1 , 1 };int sx,sy,ex,ey;bool dfs (int x, int y) if (x==ex && y==ey) return true ; st[x][y] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int nx = x + xway[i]; int ny = y + yway[i]; if (nx>=1 && ny>=1 && nx<=m && ny<=m && !st[nx][ny] && d[nx][ny]!=1 ) { if (dfs (nx,ny)) return true ; } } return false ; } void solve () cin >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { char ch; cin >> ch; if (ch=='#' ) d[i][j] = true ; else d[i][j] = false ; } memset (st,false ,sizeof st); cin >> sx >> sy >> ex >> ey; sx++; sy++; ey++; ex++; if (d[sx][sy] || d[ex][ey]) { cout << "NO" << endl; } else { if (dfs (sx,sy)) cout << "YES" << endl; else cout << "NO" << endl; } } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cin >> n; while (n--) { solve (); } }
AcWing 1113. 红与黑 BFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <iostream> #include <utility> #include <queue> #include <cstring> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e3 +10 ; bool arr[N][N];bool st[N][N];typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int n,m;int sx,sy;int dx[] = {-1 ,0 ,0 ,1 };int dy[] = {0 ,-1 ,1 ,0 };int BFS () int res =1 ; queue<PA> q; st[sx][sy] = true ; q.push ({sx,sy}); while (q.size ()) { auto tmp = q.front (); sx = tmp.first; sy = tmp.second; q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ;i < 4 ;i++) { int xx = sx + dx[i]; int yy = sy + dy[i]; if (xx < 1 || xx> m || yy < 1 || yy > n) { continue ; } if (arr[xx][yy] && !st[xx][yy]) { q.push ({xx,yy}); res++; st[xx][yy] = true ; } } } return res; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); while (1 ) { memset (st,0 ,sizeof st); cin >> n >> m; if (n==0 && m==0 ) return 0 ; for (int i = 1 ;i <= m;i++) { for (int j = 1 ;j <= n;j++) { char tmp; cin >> tmp; if (tmp == '.' ) arr[i][j] = true ; else if (tmp == '@' ) { sx = i; sy = j; arr[i][j] = true ; } else { arr[i][j] = false ; } } } cout << BFS () << endl; } }
DFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <iostream> #include <utility> #include <cstring> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e3 +10 ; bool arr[N][N];bool st[N][N];typedef pair<int , int > PA;typedef pair<PA, int > PA2;int n,m;int sx,sy;int dx[] = {-1 ,0 ,0 ,1 };int dy[] = {0 ,-1 ,1 ,0 };int dfs (int x, int y) int res = 0 ; st[x][y] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i<4 ;i++) { int xx = x + dx[i]; int yy = y + dy[i]; if (xx < 1 || xx > m || yy < 1 || yy > n) continue ; if (arr[xx][yy] && !st[xx][yy]) { res+= dfs (xx,yy); } } return res + 1 ; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); while (1 ) { memset (st,0 ,sizeof st); cin >> n >> m; if (n == 0 && m == 0 ) break ; for (int i = 1 ; i<=m;i++) for (int j = 1 ; j<=n;j++) { char tmp; cin >> tmp; if (tmp == '.' ) arr[i][j] = true ; else if (tmp == '@' ) { sx = i; sy = j; arr[i][j] = true ; } else { arr[i][j] = false ; } } cout << dfs (sx,sy) << endl; } }
DFS之搜索顺序 AcWing 1116. 马走日 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N = 10 ;int t,n,m,sx,sy,ans = 0 ;int dx[] = {1 ,-1 ,2 ,-2 ,1 ,-1 ,2 ,-2 };int dy[] = {2 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,-2 ,-2 ,-1 ,-1 };bool vis[N][N];void dfs (int x,int y,int t) if (t == n * m) { ans++; return ; } for (int i = 0 ;i < 8 ;i++) { int a = x + dx[i],b = y + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || vis[a][b]) continue ; vis[a][b] = true ; dfs (a,b,t + 1 ); vis[a][b] = false ; } } int main () cin >> t; while (t--) { ans = 0 ; memset (vis,false ,sizeof (vis)); cin >> n >> m >> sx >> sy; vis[sx][sy] = true ; dfs (sx,sy,1 ); cout << ans << endl; } return 0 ; }
AcWing 1117. 单词接龙 预处理字符串,将所有拼接的可能转化可达数组g[N][N]==重复字符串长度,然后对图进行遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 21 ;int n;string word[N]; int g[N][N];int used[N];int ans;void dfs (string dragon, int last) ans = max ((int )dragon.size (), ans); used[last] ++ ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) if (g[last][i] && used[i] < 2 ) dfs (dragon + word[i].substr (g[last][i]), i); used[last] -- ; } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> word[i]; char start; cin >> start; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++ ) { string a = word[i], b = word[j]; for (int k = 1 ; k < min (a.size (), b.size ()); k ++ ) if (a.substr (a.size () - k, k) == b.substr (0 , k)) { g[i][j] = k; break ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) if (word[i][0 ] == start) dfs (word[i], i); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
DFS之剪枝与优化 AcWing 165. 小猫爬山 这题可以使用记忆化搜索或者使用深搜暴搜
深搜暴搜
k >= res, return //剪枝,大于当前最优答案直接返回(后续更新不能使k减少)。
优先考虑决策少的组合(递归深度小)——将猫从大到小排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 20 ; int ans = N; int cat[N]; int sum[N]; int n, m; void dfs (int u, int k) if (k >= ans) return ; if (u == n) { ans = k; return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { if (sum[i] + cat[u] <= m) { sum[i] += cat[u]; dfs (u + 1 , k); sum[i] -= cat[u]; } } sum[k] = cat[u]; dfs (u + 1 , k + 1 ); sum[k] = 0 ; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cin >> cat[i]; } sort (cat, cat + n, greater <int >()); dfs (0 , 0 ); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
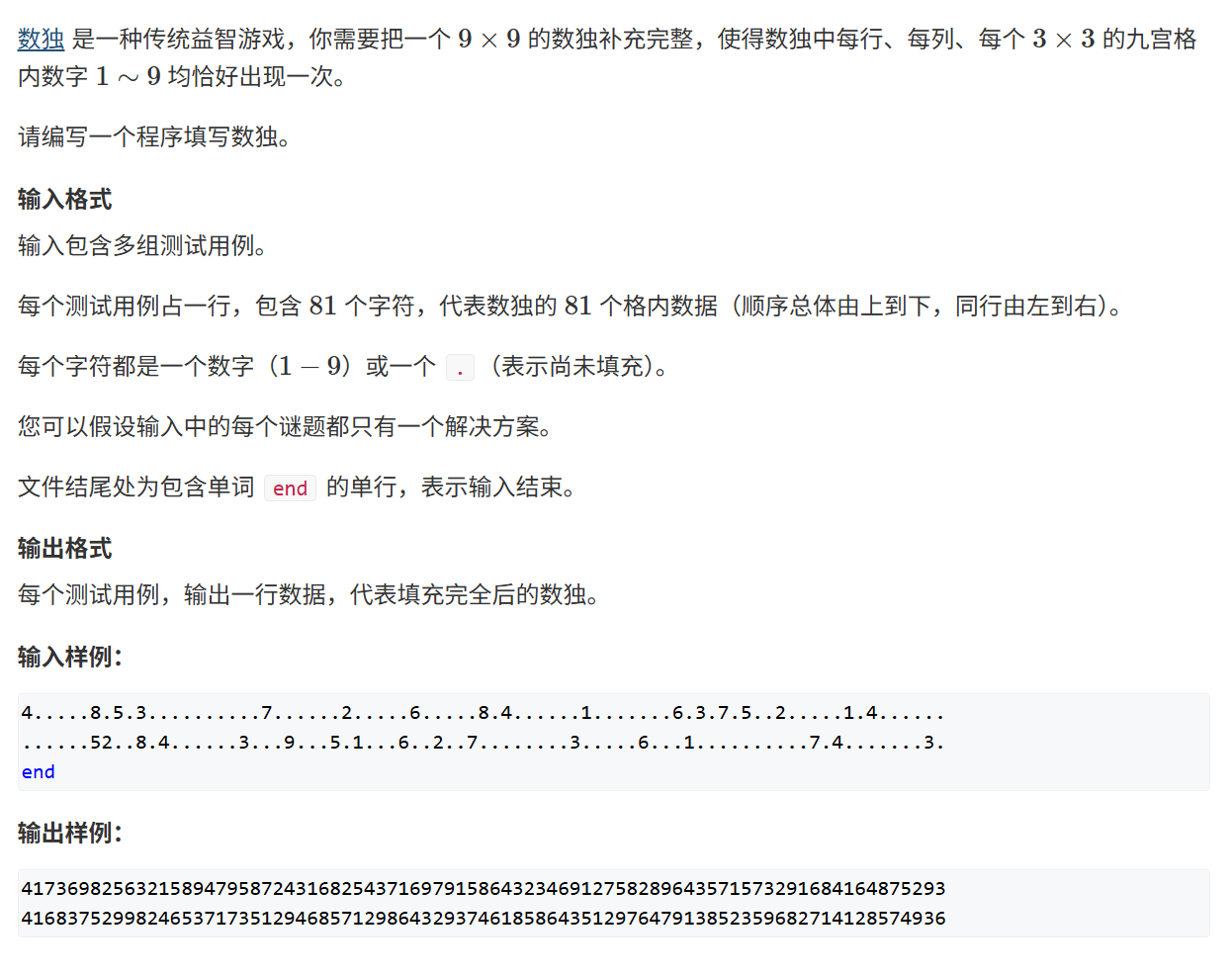
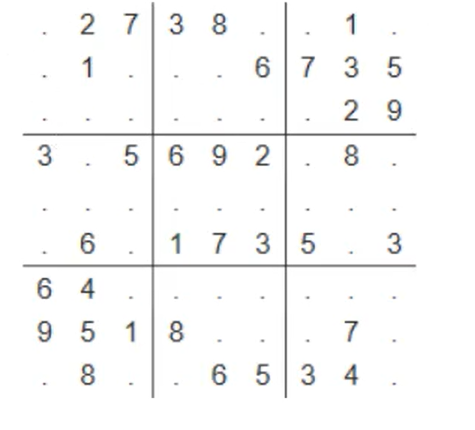
AcWing 166. 数独 要求:
每一行1-9
每一列1-9
九宫格1-9
优化:
优化搜索顺序
从当前能填合法数字最少的位置开始填数字
使用ones存储数字i的二进制1的个数
使用map存储可以当前二进制对应的数字·
排除等效冗余
任意一个状态下,我们只需要找一个位置填数即可,而不是找所有的位置和可填的数字.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 #include <cstring> #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 9 , M = 1 << N; int ones[M]; int map[M]; int row[N], col[N], cell[3 ][3 ]; char str[100 ];void init () for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i ++) row[i] = col[i] = (1 << N) - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++) for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j ++) cell[i][j] = (1 << N) - 1 ; } inline int lowbit (int x) return x & (-x); } int get (int x, int y) return row[x] & col[y] & cell[x / 3 ][y / 3 ]; } void draw (int x, int y, int t, bool is_set) if (is_set) str[x * N + y] = t + '1' ; else str[x * N + y] = '.' ; int v = 1 << t; if (!is_set) v = -v; row[x] -= v; col[y] -= v; cell[x / 3 ][y / 3 ] -= v; } bool dfs (int cnt) if (!cnt) return true ; int x, y; int minv = 10 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i ++) for (int j = 0 ; j < N; j ++) if (str[i * N + j] == '.' ) { int state = get (i,j); if (ones[state] < minv) { minv = ones[state]; x = i, y = j; } } int state = get (x, y); for (int i = state; i; i -= lowbit (i)) { int t = map[lowbit (i)]; draw (x, y, t, true ); if (dfs (cnt - 1 )) return true ; draw (x, y, t, false ); } return false ; } int main () for (int i = 0 ; i< N; i ++) map[1 << i] = i; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1 << N; i ++) for (int j = 0 ; j < N; j ++) ones[i] += (i >> j) & 1 ; while (cin >> str, str[0 ] != 'e' ) { init (); int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 , k = 0 ; i < N; i ++) for (int j = 0 ; j< N; j++, k++) if (str[k] != '.' ) { int t = str[k] - '1' ; draw (i,j,t,true ); } else cnt ++; dfs (cnt); puts (str); } return 0 ; }